A high throughput biochemical fluorometric method for measuring lipid peroxidation in HDL
- PMID: 25368900
- PMCID: PMC4219769
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111716
A high throughput biochemical fluorometric method for measuring lipid peroxidation in HDL
Abstract
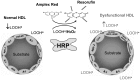
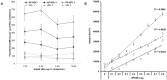
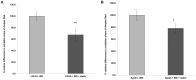
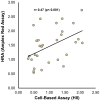
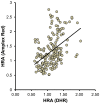
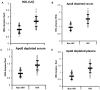
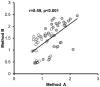
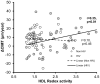
Current cell-based assays for determining the functional properties of high-density lipoproteins (HDL) have limitations. We report here the development of a new, robust fluorometric cell-free biochemical assay that measures HDL lipid peroxidation (HDLox) based on the oxidation of the fluorochrome Amplex Red. HDLox correlated with previously validated cell-based (r = 0.47, p<0.001) and cell-free assays (r = 0.46, p<0.001). HDLox distinguished dysfunctional HDL in established animal models of atherosclerosis and Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) patients. Using an immunoaffinity method for capturing HDL, we demonstrate the utility of this novel assay for measuring HDLox in a high throughput format. Furthermore, HDLox correlated significantly with measures of cardiovascular diseases including carotid intima media thickness (r = 0.35, p<0.01) and subendocardial viability ratio (r = -0.21, p = 0.05) and physiological parameters such as metabolic and anthropometric parameters (p<0.05). In conclusion, we report the development of a new fluorometric method that offers a reproducible and rapid means for determining HDL function/quality that is suitable for high throughput implementation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

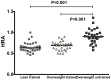
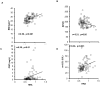
References
-
- Navab M, Reddy ST, Van Lenten BJ, Fogelman AM (2011) HDL and cardiovascular disease: atherogenic and atheroprotective mechanisms. Nat Rev Cardiol 8: 222–232 nrcardio.2010.222 [pii]; 10.1038/nrcardio.2010.222 [doi]. - PubMed
-
- Patel PJ, Khera AV, Jafri K, Wilensky RL, Rader DJ (2011) The anti-oxidative capacity of high-density lipoprotein is reduced in acute coronary syndrome but not in stable coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 58: 2068–2075 S0735-1097(11)03137-8 [pii]; 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.08.030 [doi]. - PubMed
-
- Patel S, Drew BG, Nakhla S, Duffy SJ, Murphy AJ, et al. (2009) Reconstituted high-density lipoprotein increases plasma high-density lipoprotein anti-inflammatory properties and cholesterol efflux capacity in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Am Coll Cardiol 53: 962–971 S0735-1097(08)04128-4 [pii]; 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.12.008 [doi]. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI28697/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071776/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK090406/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08AI08272/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL082823/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01HL095126/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HL105188/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL082823/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK090406/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI108272/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL095126/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL095132/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL095132/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI028697/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

