Multipinhole collimator with 20 apertures for a brain SPECT application
- PMID: 25370660
- PMCID: PMC4218691
- DOI: 10.1118/1.4897567
Multipinhole collimator with 20 apertures for a brain SPECT application
Abstract
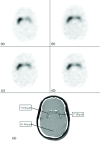
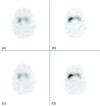
Purpose: Several new technologies for single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) instrumentation with parallel-hole collimation have been proposed to improve detector sensitivity and signal collection efficiency. Benefits from improved signal efficiency include shorter acquisition times and lower dose requirements. In this paper, the authors show a possibility of over an order of magnitude enhancement in photon detection efficiency (from 7.6 × 10(-5) to 1.6 × 10(-3)) for dopamine transporter (DaT) imaging of the striatum over the conventional SPECT parallel-hole collimators by use of custom-designed 20 multipinhole (20-MPH) collimators with apertures of 0.75 cm diameter.
Methods: Quantifying specific binding ratio (SBR) of (123)I-ioflupane or (123)I-iometopane's signal at the striatal region is a common brain imaging method to confirm the diagnosis of the Parkinson's disease. The authors performed imaging of a striatal phantom filled with aqueous solution of I-123 and compared camera recovery ratios of SBR acquired between low-energy high-resolution (LEHR) parallel-hole collimators and 20-MPH collimators.
Results: With only two-thirds of total acquisition time (20 min against 30 min), a comparable camera recovery ratio of SBR was achieved using 20-MPH collimators in comparison to that from the LEHR collimator study.
Conclusions: Their systematic analyses showed that the 20-MPH collimator could be a promising alternative for the DaT SPECT imaging for brain over the traditional LEHR collimator, which could give both shorter scan time and improved diagnostic accuracy.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Design and evaluation of two multi-pinhole collimators for brain SPECT.Ann Nucl Med. 2017 Oct;31(8):636-648. doi: 10.1007/s12149-017-1195-y. Epub 2017 Jul 28. Ann Nucl Med. 2017. PMID: 28755084
-
Performance evaluation of a novel multi-pinhole collimator for dopamine transporter SPECT.Phys Med Biol. 2020 Aug 21;65(16):165015. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ab9067. Phys Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32369781
-
Cross-camera comparison of SPECT measurements of a 3-D anthropomorphic basal ganglia phantom.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2006 Apr;33(4):495-502. doi: 10.1007/s00259-005-0036-8. Epub 2006 Jan 25. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2006. PMID: 16435116
-
Dopamine transporter SPECT imaging in Parkinson’s disease and parkinsonian disorders.Turk J Med Sci. 2021 Apr 30;51(2):400-410. doi: 10.3906/sag-2008-253. Turk J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33237660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the superselective radioligand [123I]PE2I for imaging of the dopamine transporter in SPECT.Dan Med Bull. 2011 May;58(5):B4279. Dan Med Bull. 2011. PMID: 21535991 Review.
Cited by
-
Design of a Multi-Pinhole Collimator for I-123 DaTscan Imaging on Dual-Headed SPECT Systems in Combination with a Fan-Beam Collimator.IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2016 Feb;63(1):90-97. doi: 10.1109/TNS.2016.2515519. Epub 2016 Feb 3. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2016. PMID: 27182078 Free PMC article.
-
Design Study of an Ultrahigh Resolution Brain SPECT System Using a Synthetic Compound-Eye Camera Design With Micro-Slit and Micro-Ring Apertures.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2021 Dec;40(12):3711-3727. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2021.3096920. Epub 2021 Nov 30. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2021. PMID: 34255626 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical utilities of multi-pinhole single photon emission computed tomography.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2020 Oct;10(10):2006-2029. doi: 10.21037/qims-19-1036. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2020. PMID: 33014732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple-pinhole collimators improve intra- and between-rater agreement and the certainty of the visual interpretation in dopamine transporter SPECT.EJNMMI Res. 2022 Aug 17;12(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s13550-022-00923-w. EJNMMI Res. 2022. PMID: 35976493 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of Axial and Angular Sampling in Multi-Detector Pinhole-SPECT Brain Imaging.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2020 Dec;39(12):4209-4224. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2020.3015079. Epub 2020 Nov 30. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32763850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hornykiewicz O., “Dopamine (3-hydroxytyramine) and brain function,” Pharmacol. Rev. 18, 925–964 (1966). - PubMed
-
- Hughes A. J., Ben-Shlomo Y., Daniel S. E., and Lees A. J., “What features improve the accuracy of clinical diagnosis in Parkinson’s disease: A clinicopathologic study,” Neurology 57, S34–S38 (1992). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

