Impact of biologic agents with and without concomitant methotrexate and at reduced doses in older rheumatoid arthritis patients
- PMID: 25370912
- PMCID: PMC4412783
- DOI: 10.1002/acr.22510
Impact of biologic agents with and without concomitant methotrexate and at reduced doses in older rheumatoid arthritis patients
Abstract
Objective: To examine whether concomitant methotrexate (MTX) use is associated with better biologic persistence and whether self-administered anti-tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) therapies are used at reduced doses in real-world clinical care settings, not just clinical trials.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study among rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients using Medicare claims data from 2006 to 2012. Subjects were new initiators of etanercept, infliximab, adalimumab, abatacept, and tocilizumab with at least 12 months of continuous medical and pharmacy coverage after treatment initiation. We examined the association between concomitant MTX use and persistence on biologic agents using Cox proportional hazards regression, adjusting for demographics and baseline comorbidities. We further identified a subgroup of patients who initiated and were adherent on etanercept or adalimumab for at least 12 months and examined the proportion of patients who subsequently used these therapies at reduced doses continuously for an additional 12, 18, and 24 months.
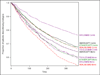
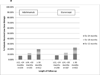
Results: Of 26,510 eligible RA patients, 10,511 initiated biologic monotherapy. Overall, patients who initiated biologic monotherapy were 1.4 (95% confidence interval [95% CI] 1.3-1.5) times more likely to discontinue at 1 year compared to those who initiated combination therapy, and 1.8 (95% CI 1.7-2.0) times more likely if starting infliximab monotherapy. Approximately 10-20% of patients who initiated and adhered to etanercept and adalimumab for ≥12 months subsequently received reduced-dose therapy for an 12 additional months and beyond.
Conclusion: In real-world practice, concomitant MTX was associated with improved persistence on biologic therapy, especially for infliximab users; reduced-dose injectable anti-TNF therapy was used by a substantial proportion of RA patients.
© 2015, American College of Rheumatology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Twelve-Year Retention Rate of First-Line Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Real-Life Data From a Local Registry.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2016 Apr;68(4):432-9. doi: 10.1002/acr.22788. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2016. PMID: 26556048
-
Treatment persistence with adalimumab, etanercept, or infliximab in combination with methotrexate and the effects on health care costs in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Ther. 2008 Jul;30(7):1375-84. doi: 10.1016/s0149-2918(08)80063-x. Clin Ther. 2008. PMID: 18691998
-
National and regional dose escalation and cost of tumor necrosis factor blocker therapy in biologic-naïve rheumatoid arthritis patients in US health plans.J Med Econ. 2014 Jan;17(1):1-10. doi: 10.3111/13696998.2013.856314. Epub 2013 Oct 31. J Med Econ. 2014. PMID: 24131136
-
[Biologic therapy with anti-TNFα in rheumathoid arthritis].Reumatismo. 2005;57(4 Suppl):17-21. Reumatismo. 2005. PMID: 16385351 Review. Italian.
-
Review of eight pharmacoeconomic studies of the value of biologic DMARDs (adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab) in the management of rheumatoid arthritis.J Manag Care Pharm. 2006 Sep;12(7):555-69. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2006.12.7.555. J Manag Care Pharm. 2006. PMID: 16981801 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Combination therapy with biologic agents in rheumatic diseases: current and future prospects.Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2016 Oct;8(5):192-202. doi: 10.1177/1759720X16665330. Epub 2016 Aug 29. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2016. PMID: 27721905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors associated with long-term retention of treatment with golimumab in a real-world setting: an analysis of the Spanish BIOBADASER registry.Rheumatol Int. 2019 Mar;39(3):509-515. doi: 10.1007/s00296-018-4177-z. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Rheumatol Int. 2019. PMID: 30353269
-
Medication adherence and persistence in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and psoriatic arthritis: a systematic literature review.Patient Prefer Adherence. 2018 Aug 21;12:1483-1503. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S167508. eCollection 2018. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2018. PMID: 30174415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does biologic survival depend on co-prescribed methotrexate dose in established rheumatoid arthritis? A real-world study.Eur J Rheumatol. 2019 Nov 25;7(1):21-25. doi: 10.5152/eurjrheum.2019.19048. Print 2020 Jan. Eur J Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 31782724 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and Efficacy of Biological Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs in Older Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: Staying the Distance.Drugs Aging. 2016 Jun;33(6):387-98. doi: 10.1007/s40266-016-0374-1. Drugs Aging. 2016. PMID: 27154398 Review.
References
-
- Singh JA, Furst DE, Bharat A, Curtis JR, Kavanaugh AF, Kremer JM, Moreland LW, O'Dell J, Winthrop KL, Beukelman T, et al. 2012 update of the 2008 American College of Rheumatology recommendations for the use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and biologic agents in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2012;64(5):625–639. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Moreland LW, O'Dell JR, Paulus HE, Curtis JR, Bathon JM, William St Clair E, Louis Bridges S, Jr, Zhang J, McVie T, Howard G, et al. A randomized comparative effectiveness study of oral triple therapy versus etanercept plus methotrexate in early, aggressive rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bathon JM, Martin RW, Fleischmann RM, Tesser JR, Schiff MH, Keystone EC, Genovese MC, Wasko MC, Moreland LW, Weaver AL, et al. A comparison of etanercept and methotrexate in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(22):1586–1593. - PubMed
-
- Lipsky PE, van der Heijde DM, St Clair EW, Furst DE, Breedveld FC, Kalden JR, Smolen JS, Weisman M, Emery P, Feldmann M, et al. Infliximab and methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Trial in Rheumatoid Arthritis with Concomitant Therapy Study Group. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(22):1594–1602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

