Traditional Chinese medicine, Qing Ying Tang, ameliorates the severity of acute lung injury induced by severe acute pancreatitis in rats via the upregulation of aquaporin-1
- PMID: 25371738
- PMCID: PMC4218699
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2014.1987
Traditional Chinese medicine, Qing Ying Tang, ameliorates the severity of acute lung injury induced by severe acute pancreatitis in rats via the upregulation of aquaporin-1
Abstract
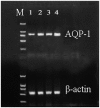
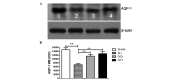
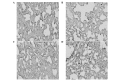
Aquaporin-1 (AQP-1) is expressed in lung endothelial cells and regulates water transport; thus, AQP-1 plays an important role in a number of edema-associated lung diseases. Qing Yin Tang (QYT), a traditional Chinese medicine, has been shown to effectively reduce the mortality rate of acute lung injury (ALI) induced by severe acute pancreatitis (SAP). The current study aimed to investigate the detailed mechanisms underlying the effects of QYT on ALI induced by SAP, particularly the effects on the expression levels of AQP-1 in the lung tissue. ALI was established in Wister rats who were subsequently divided into four groups: SHAM, ALI, dexamethasone (DEX) and QYT groups (n=8 per group). In the QYT group, 20 ml/kg QYT was administered by gavage immediately following the induction of SAP. Blood and lung tissues were collected 8 h following the induction of pancreatitis. The lung wet/dry ratio, as well as the levels of blood gases, serum amylase and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), were measured at 4, 8 and 12 h following SAP-associated ALI induction surgery. The expression levels of AQP-1 in the lung tissue were detected by quantitative polymerase chain reaction, immunohistochemistry and western blot analysis. No statistically significant differences were observed with regard to the levels of serum amylase, wet/dry ratio, partial pressure of oxygen, serum TNF-α and pathological changes in the pulmonary tissue between the QYT and DEX groups; however, a statistically significant difference was observed when compared with the ALI group. The expression levels of AQP-1 significantly increased (P<0.05) and lung edema was alleviated in the QYT and DEX groups, when compared with ALI group. Therefore, the expression level of AQP-1 is associated with pulmonary edema. QYT protects the lungs from injury induced by SAP via the upregulation of AQP-1, which suppresses TNF-α expression.
Keywords: acute lung injury; aquaporin-1; qing yin tang; severe acute pancreatitis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Expression of secretory type II phospholipase A₂ in acute lung injury following acute pancreatitis and interventional effect of Qingyi decoction on it].Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2010 Sep;22(9):518-21. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2010. PMID: 20854728 Chinese.
-
Emodin ameliorates acute lung injury induced by severe acute pancreatitis through the up-regulated expressions of AQP1 and AQP5 in lung.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016 Nov;43(11):1071-1079. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12627. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27452155
-
Dai-Huang-Fu-Zi-Tang alleviates pulmonary and intestinal injury with severe acute pancreatitis via regulating aquaporins in rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Jun 2;17(1):288. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1789-x. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28577538 Free PMC article.
-
From pancreas to lungs: The role of immune cells in severe acute pancreatitis and acute lung injury.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024 Jul;12(7):e1351. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1351. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024. PMID: 39023414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intestinal Mucosal Immune Barrier: A Powerful Firewall Against Severe Acute Pancreatitis-Associated Acute Lung Injury via the Gut-Lung Axis.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Apr 10;17:2173-2193. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S448819. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38617383 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Applying Hot Compresses with Rhubarb and Mirabilite to Reduce Pancreatic Leakage Occurrence in the Treatment of Severe Acute Pancreatitis.Iran J Public Health. 2017 Jan;46(1):136-138. Iran J Public Health. 2017. PMID: 28451541 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The mechanism underlying alpinetin-mediated alleviation of pancreatitis-associated lung injury through upregulating aquaporin-1.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016 Feb 24;10:841-50. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S97614. eCollection 2016. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016. PMID: 26966354 Free PMC article.
-
Aquaporins in lung health and disease: Emerging roles, regulation, and clinical implications.Respir Med. 2020 Nov-Dec;174:106193. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2020.106193. Epub 2020 Oct 17. Respir Med. 2020. PMID: 33096317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Seawater-drowning-induced acute lung injury: From molecular mechanisms to potential treatments.Exp Ther Med. 2017 Jun;13(6):2591-2598. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4302. Epub 2017 Apr 5. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 28587319 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of nimesulide on acute lung injury in mice with severe acute pancreatitis.Am J Transl Res. 2019 Sep 15;11(9):6024-6031. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 31632570 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agre P, Bonhivers M, Borgnia MJ. The aquaporins, blueprints for cellular plumbing systems. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:14659–14662. - PubMed
-
- Benga G. On the definition, nomenclature and classification of water channel proteins (aquaporins and relatives) Mol Aspects Med. 2012;33:514–517. - PubMed
-
- Denker BM, Smith BL, Kuhajda FP, Agre P. Identification, purification, and partial characterization of a novel Mr 28,000 integral membrane protein from erythrocytes and renal tubules. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:15634–15642. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
