Brain-derived neurotrophic factor exerts neuroprotective actions against amyloid β-induced apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells
- PMID: 25371750
- PMCID: PMC4218707
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2014.2033
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor exerts neuroprotective actions against amyloid β-induced apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells
Abstract
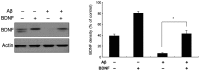
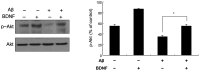
Alzheimer's disease (AD) brains demonstrate decreased levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and increased levels of β-amyloid peptide (Aβ), which is neurotoxic. The present study assessed the impact of BDNF on the toxic effects of Aβ25-35-induced apoptosis and the effects on BDNF-mediated signaling using the MTT assay, western blotting and reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Aβ25-35 was found to induce an apoptosis, dose-dependent effect on SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells, which peaked at a concentration of 20 μM after 24 h. A combination of Aβ25-35 and BDNF treatment increased the levels of Akt and decreased the level of glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK3β) in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. These findings indicated that BDNF administration exerted a neuroprotective effect against the toxicity of the Aβ25-35-induced apoptosis in these cells, which was accompanied by phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt activation and GSK3β phosphorylation. The mechanisms and signaling pathways underlying neuronal degeneration induced by the Aβ peptide remain to be further elucidated.
Keywords: Akt; brain-derived neurotrophic factor; glycogen synthase kinase 3β; neuroblastoma cell; β-amyloid peptide.
Figures





Similar articles
-
An Extract from Shrimp Processing By-Products Protects SH-SY5Y Cells from Neurotoxicity Induced by Aβ25-35.Mar Drugs. 2017 Mar 22;15(3):83. doi: 10.3390/md15030083. Mar Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28327516 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment with the neurotoxic Aβ (25-35) peptide modulates the expression of neuroprotective factors Pin1, Sirtuin 1, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells.Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2016 May;68(5):271-6. doi: 10.1016/j.etp.2016.02.001. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26915812
-
The protective underlying mechanisms of Schisandrin on SH-SY5Y cell model of Alzheimer's disease.J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2019;82(19):1019-1026. doi: 10.1080/15287394.2019.1684007. Epub 2019 Nov 18. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2019. PMID: 31739764
-
N-Feruloyl Serotonin Attenuates Neuronal Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in Aβ25-35-Treated Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells.Molecules. 2023 Feb 7;28(4):1610. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041610. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36838597 Free PMC article.
-
The link between sarcopenic obesity and Alzheimer's disease: a brain-derived neurotrophic factor point of view.J Physiol. 2025 Feb 12. doi: 10.1113/JP288032. Online ahead of print. J Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39937973 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Depression.Shanghai Arch Psychiatry. 2018 Apr 25;30(2):84-92. doi: 10.11919/j.issn.1002-0829.217047. Shanghai Arch Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29736128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in main neurodegenerative diseases.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Mar;18(3):554-555. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.350199. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 36018175 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Bone marrow stromal cells in Modic type 1 changes promote neurite outgrowth.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Oct 25;11:1286280. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1286280. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37965581 Free PMC article.
-
The Conspicuous Link between Ear, Brain and Heart-Could Neurotrophin-Treatment of Age-Related Hearing Loss Help Prevent Alzheimer's Disease and Associated Amyloid Cardiomyopathy?Biomolecules. 2021 Jun 17;11(6):900. doi: 10.3390/biom11060900. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34204299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Vesicle Trafficking Defects in the Pathogenesis of Prion and Prion-Like Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 23;21(19):7016. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197016. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32977678 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mesulam MM. Neuroplasticity failure in Alzheimer’s disease: bridging the gap between plaques and tangles. Neuron. 1999;24:521–529. - PubMed
-
- Dickson DW. Neuropathology of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias. Clin Geriatr Med. 2001;17:209–228. - PubMed
-
- Selkoe DJ. Alzheimer’s disease is a synaptic failure. Science. 2002;298:789–791. - PubMed
-
- Yankner BA. Mechanisms of neuronal degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron. 1996;16:921–932. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
