Mathematical Modeling of HIV Dynamics After Antiretroviral Therapy Initiation: A Review
- PMID: 25371860
- PMCID: PMC4215334
- DOI: 10.1089/biores.2014.0024
Mathematical Modeling of HIV Dynamics After Antiretroviral Therapy Initiation: A Review
Abstract
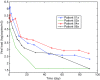
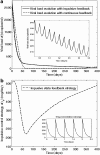
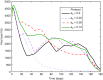
This review shows the potential ground-breaking impact that mathematical tools may have in the analysis and the understanding of the HIV dynamics. In the first part, early diagnosis of immunological failure is inferred from the estimation of certain parameters of a mathematical model of the HIV infection dynamics. This method is supported by clinical research results from an original clinical trial: data just after 1 month following therapy initiation are used to carry out the model identification. The diagnosis is shown to be consistent with results from monitoring of the patients after 6 months. In the second part of this review, prospective research results are given for the design of individual anti-HIV treatments optimizing the recovery of the immune system and minimizing side effects. In this respect, two methods are discussed. The first one combines HIV population dynamics with pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics models to generate drug treatments using impulsive control systems. The second one is based on optimal control theory and uses a recently published differential equation to model the side effects produced by highly active antiretroviral therapy therapies. The main advantage of these revisited methods is that the drug treatment is computed directly in amounts of drugs, which is easier to interpret by physicians and patients.
Keywords: AIDS; HIV; aid for diagnosis; apoptosis; dynamical systems; modeling; nonlinear control; pharmacodynamics; pharmacokinetics.
Figures


References
-
- Ho DD, Neumann AU, Perelson AS, et al. . Rapid turnover of plasma virions and CD4 lymphocytes in HIV-1 infection. Nature. 1995;373:123–126 - PubMed
-
- Perelson AS, Essunger P, Cao Y, et al. . Decay characteristics of HIV-1-infected compartments during combination therapy. Nature. 1997;387:188–191 - PubMed
-
- Perelson AS, Nelson PW. Mathematical analysis of HIV-1 dynamics in vivo. SIAM Review. 1999;41:3–44
-
- Mhawej MJ, Brunet-François C, Fonteneau R, et al. . Apoptosis characterizes immunological failure of HIV infected patients. Control Engineering Practice. 2009;17:798–804
-
- Ouattara DA. Mathematical analysis of the HIV-1 infection: Parameter estimation, therapies effectiveness, and therapeutical failures. In 27th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Shanghai, China, September 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
