Impact of change in delivery practice on neonatal and maternal outcomes in cases of significant congenital heart disease
- PMID: 25371936
- PMCID: PMC4221808
- DOI: 10.1111/chd.12167
Impact of change in delivery practice on neonatal and maternal outcomes in cases of significant congenital heart disease
Abstract
Objective: Because of data published in 2009 demonstrating improved outcomes among early- vs. late-term infants,practice shifted toward delivering infants at later gestational ages. We examined the effects of this change on neonates with congenital heart disease.
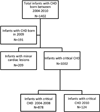
Design: This was a retrospective cohort study. Neonates with congenital heart disease born between 2004 and 2008 were compared with those born in 2010. Patients born in 2009, considered to be a transitional year, were excluded.
Setting: Our study was conducted at a tertiary care level 4 neonatal intensive care unit with comprehensive cardiac service.
Patients: Study subjects consisted of neonates with significant congenital heart disease admitted between 2004 and 2010.
Outcome measures: Outcomes measures consisted of mode of delivery, length of stay, neonatal morbidity, and mortality.
Results: There were 878 infants with congenital heart disease born in 2004-2008 and 124 in 2010. The mean gestational age was higher in 2010 than in 2004-2008 (38.4 ± 1.9 vs. 37.8 ± 2.3 weeks, P = .001), and there were fewer preterm births in 2010 compared with 2004-2008 (P = .003, odds ratio [OR] = 0.4). Mean birth weight was also higher in 2010 (3134 ± 675 vs. 2975 ± 599 g, P = .008). In 2010, less than half as many infants were born via scheduled induction (P < .001, OR = 0.2) or scheduled cesarean delivery (P = .002, OR = 0.4) as in 2004-2008. However, in 2010, there were more urgent inductions (P = .002, OR = 3.1), cesarean deliveries after labor (P = .01, OR = 2.2),and unplanned cesarean deliveries in general (P = .02, OR = 1.7) compared with 2004-2008. In 2010, neonates were less likely to require preoperative vasopressors (P = .002), but there were no differences in 5 minutes APGAR,antibiotic administration, preoperative intubation, median length of stay, or mortality compared with 2004-2008.Conclusions. Despite increased gestational age and birth weight following the shift in delivery practice, there was no difference in length of stay, neonatal morbidity, or mortality in infants with congenital heart disease. The resultant increase in urgent cesarean delivery and urgent inductions may confer additional maternal morbidity.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
None
Figures
References
-
- De Luca R, Boulvain M, Irion O, Berner M, Pfister RE. Incidence of early neonatal mortality and morbidity after late-preterm and term cesarean delivery. Pediatrics. 2009 Jun;123(6):e1064–e1071. - PubMed
-
- Andrews RE, Simpson JM, Sharland GK, Sullivan ID, Yates RW. Outcome after preterm delivery of infants antenatally diagnosed with congenital heart disease. J Pediatr. 2006 Feb;148(2):213–216. - PubMed
-
- Jenkins KJ, Gauvreau K, Newburger JW, Spray TL, Moller JH, Iezzoni LI. Consensus-based method for risk adjustment for surgery for congenital heart disease. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2002 Jan;123(1):110–118. - PubMed
-
- Cheng YW, Nicholson JM, Nakagawa S, Bruckner TA, Washington AE, Caughey AB. Perinatal outcomes in low-risk term pregnancies: do they differ by week of gestation? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008 Oct;199(4):370 e1–370 e7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical