Impact of the superoxide dismutase 2 Val16Ala polymorphism on the relationship between valproic acid exposure and elevation of γ-glutamyltransferase in patients with epilepsy: a population pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic analysis
- PMID: 25372290
- PMCID: PMC4220988
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111066
Impact of the superoxide dismutase 2 Val16Ala polymorphism on the relationship between valproic acid exposure and elevation of γ-glutamyltransferase in patients with epilepsy: a population pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic analysis
Expression of concern in
-
Expression of Concern: Impact of the Superoxide Dismutase 2 Val16Ala Polymorphism on the Relationship between Valproic Acid Exposure and Elevation of γ-Glutamyltransferase in Patients with Epilepsy: A Population Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Jan 11;18(1):e0279162. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0279162. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36630339 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: There has been accumulating evidence that there are associations among γ-glutamyltransferase (γ-GT) elevation and all-cause mortality, cardiovascular diseases and metabolic diseases, including nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. The primary objective of this study was to evaluate the impact of the most common and potentially functional polymorphisms of antioxidant enzyme genes, i.e. superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2), glutathione S-transferase M1 and glutathione S-transferase T1, on the γ-GT elevation during valproic acid (VPA) therapy.
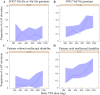
Methods and findings: This retrospective study included 237 and 169 VPA-treated Japanese patients with epilepsy for population pharmacokinetic and pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic analyses, respectively. A nonlinear mixed-effect model represented the pharmacokinetics of VPA and the relationships between VPA exposure and γ-GT elevation. A one-compartment model of the pharmacokinetic parameters of VPA adequately described the data; while the model for the probability of the γ-GT elevation was fitted using a logistic regression model, in which the logit function of the probability was a linear function of VPA exposure. The SOD2 Val16Ala polymorphism and complication with intellectual disability were found to be significant covariates influencing the intercept of the logit function for the probability of an elevated γ-GT level. The predicted mean percentages of the subjects with γ-GT elevation were about 2- to 3-fold, 3- to 4-fold and 4- to 8-fold greater in patients with the SOD2 Val/Val genotype but without any intellectual disability, those with the SOD2 Val/Ala or Ala/Ala genotype and intellectual disability and those with the SOD2 Val/Val genotype and intellectual disability, respectively, compared to those with the SOD2 Val/Ala or Ala/Ala genotype without intellectual disability.
Conclusion: Our results showed that the SOD2 Val16Ala polymorphism has an impact on the relationship between VPA exposure and γ-GT elevation in patients with epilepsy. These results suggest that determining the SOD2 genotype could be helpful for preventing the VPA-induced γ-GT elevation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Superoxide dismutase 2 Val16Ala polymorphism is a risk factor for the valproic acid-related elevation of serum aminotransferases.Epilepsy Res. 2012 Mar;99(1-2):183-6. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2011.10.033. Epub 2011 Nov 25. Epilepsy Res. 2012. PMID: 22119635
-
Determination of the Optimal Concentration of Valproic Acid in Patients with Epilepsy: A Population Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Analysis.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 20;10(10):e0141266. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141266. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26484865 Free PMC article.
-
Catalase C-262T Polymorphism Is a Risk Factor for Valproic Acid-Induced Abnormal Liver Function in Chinese Patients With Epilepsy.Ther Drug Monit. 2019 Feb;41(1):91-96. doi: 10.1097/FTD.0000000000000574. Ther Drug Monit. 2019. PMID: 30422963
-
Effect of UGT2B7 genotypes on plasma concentration of valproic acid: a meta-analysis.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2018 Apr;74(4):433-442. doi: 10.1007/s00228-017-2395-z. Epub 2017 Dec 14. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29243113 Review.
-
The effects of rosuvastatin on lipid-lowering, inflammatory, antioxidant and fibrinolytics blood biomarkers are influenced by Val16Ala superoxide dismutase manganese-dependent gene polymorphism.Pharmacogenomics J. 2016 Nov;16(6):501-506. doi: 10.1038/tpj.2015.91. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Pharmacogenomics J. 2016. PMID: 26882122 Review.
Cited by
-
Population pharmacokinetics of valproic acid in adult Chinese patients with bipolar disorder.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2022 Mar;78(3):405-418. doi: 10.1007/s00228-021-03246-2. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34854947
-
Pharmacogenomics in epilepsy.Neurosci Lett. 2018 Feb 22;667:27-39. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.01.014. Epub 2017 Jan 10. Neurosci Lett. 2018. PMID: 28082152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retrospective Analysis of Steady-State Sodium Valproate Plasma Concentrations in Chinese Patients With Bipolar Disorder: Impact of Demographic and Clinical Characteristics.Ther Drug Monit. 2024 Oct 1;46(5):658-663. doi: 10.1097/FTD.0000000000001199. Epub 2024 Apr 19. Ther Drug Monit. 2024. PMID: 38648661 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of population pharmacokinetics of valproic acid.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018 May;84(5):816-834. doi: 10.1111/bcp.13510. Epub 2018 Feb 28. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29328514 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Concern: Impact of the Superoxide Dismutase 2 Val16Ala Polymorphism on the Relationship between Valproic Acid Exposure and Elevation of γ-Glutamyltransferase in Patients with Epilepsy: A Population Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Jan 11;18(1):e0279162. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0279162. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36630339 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Whitfield JB (2001) Gamma glutamyl transferase. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 38: 263–355. - PubMed
-
- Verrijken A, Francque S, Mertens I, Talloen M, Peiffer F, et al. (2010) Visceral adipose tissue and inflammation correlate with elevated liver tests in a cohort of overweight and obese patients. Int J Obes (Lond) 34: 899–907. - PubMed
-
- Lioudaki E, Ganotakis ES, Mikhailidis DP (2011) Liver enzymes: potential cardiovascular risk markers? Curr Pharm Des 17: 3632–3643. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

