Structural basis for the recognition of muramyltripeptide by Helicobacter pylori Csd4, a D,L-carboxypeptidase controlling the helical cell shape
- PMID: 25372672
- PMCID: PMC4220969
- DOI: 10.1107/S1399004714018732
Structural basis for the recognition of muramyltripeptide by Helicobacter pylori Csd4, a D,L-carboxypeptidase controlling the helical cell shape
Abstract
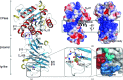
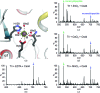
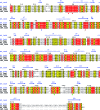
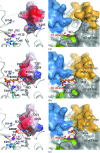
Helicobacter pylori infection causes a variety of gastrointestinal diseases, including peptic ulcers and gastric cancer. Its colonization of the gastric mucosa of the human stomach is a prerequisite for survival in the stomach. Colonization depends on its motility, which is facilitated by the helical shape of the bacterium. In H. pylori, cross-linking relaxation or trimming of peptidoglycan muropeptides affects the helical cell shape. Csd4 has been identified as one of the cell shape-determining peptidoglycan hydrolases in H. pylori. It is a Zn(2+)-dependent D,L-carboxypeptidase that cleaves the bond between the γ-D-Glu and the mDAP of the non-cross-linked muramyltripeptide (muramyl-L-Ala-γ-D-Glu-mDAP) of the peptidoglycan to produce the muramyldipeptide (muramyl-L-Ala-γ-D-Glu) and mDAP. Here, the crystal structure of H. pylori Csd4 (HP1075 in strain 26695) is reported in three different states: the ligand-unbound form, the substrate-bound form and the product-bound form. H. pylori Csd4 consists of three domains: an N-terminal D,L-carboxypeptidase domain with a typical carboxypeptidase fold, a central β-barrel domain with a novel fold and a C-terminal immunoglobulin-like domain. The D,L-carboxypeptidase domain recognizes the substrate by interacting primarily with the terminal mDAP moiety of the muramyltripeptide. It undergoes a significant structural change upon binding either mDAP or the mDAP-containing muramyltripeptide. It it also shown that Csd5, another cell-shape determinant in H. pylori, is capable of interacting not only with H. pylori Csd4 but also with the dipeptide product of the reaction catalyzed by Csd4.
Keywords: HP1075; Helicobacter pylori; cell shape; csd4; csd5; d,l-carboxypeptidase; meso-diaminopimelate; peptidoglycan; pgp1.
Figures

References
-
- Adams, P. D. et al. (2010). Acta Cryst. D66, 213–221. - PubMed
-
- Berg, H. C. & Turner, L. (1979). Nature (London), 278, 349–351. - PubMed
-
- Bonis, M., Ecobichon, C., Guadagnini, S., Prévost, M. C. & Boneca, I. G. (2010). Mol. Microbiol. 78, 809–819. - PubMed
-
- Bunnage, M. E. et al. (2007). J. Med. Chem. 50, 6095–6103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

