Nonclassical Ly6C(-) monocytes drive the development of inflammatory arthritis in mice
- PMID: 25373902
- PMCID: PMC4223808
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.09.032
Nonclassical Ly6C(-) monocytes drive the development of inflammatory arthritis in mice
Abstract
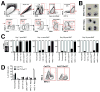
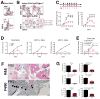
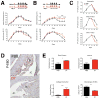
Different subsets and/or polarized phenotypes of monocytes and macrophages may play distinct roles during the development and resolution of inflammation. Here, we demonstrate in a murine model of rheumatoid arthritis that nonclassical Ly6C(-) monocytes are required for the initiation and progression of sterile joint inflammation. Moreover, nonclassical Ly6C(-) monocytes differentiate into inflammatory macrophages (M1), which drive disease pathogenesis and display plasticity during the resolution phase. During the development of arthritis, these cells polarize toward an alternatively activated phenotype (M2), promoting the resolution of joint inflammation. The influx of Ly6C(-) monocytes and their subsequent classical and then alternative activation occurs without changes in synovial tissue-resident macrophages, which express markers of M2 polarization throughout the course of the arthritis and attenuate joint inflammation during the initiation phase. These data suggest that circulating Ly6C(-) monocytes recruited to the joint upon injury orchestrate the development and resolution of autoimmune joint inflammation.
Figures
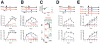


References
-
- Auffray C, Fogg D, Garfa M, Elain G, Join-Lambert O, Kayal S, Sarnacki S, Cumano A, Lauvau G, Geissmann F. Monitoring of blood vessels and tissues by a population of monocytes with patrolling behavior. Science. 2007;317:666–670. - PubMed
-
- Auffray C, Sieweke MH, Geissmann F. Blood monocytes: development, heterogeneity, and relationship with dendritic cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:669–692. - PubMed
-
- Bruhns P, Samuelsson A, Pollard JW, Ravetch JV. Colony-stimulating factor-1-dependent macrophages are responsible for IVIG protection in antibody-induced autoimmune disease. Immunity. 2003;18:573–581. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 19791/VAC_/Versus Arthritis/United Kingdom
- R01 ES013995/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR064546/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR050250/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA060553/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI092490/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR054796/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- 20088/ARC_/Arthritis Research UK/United Kingdom
- K01 AR064313/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR054796/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- 19614/ARC_/Arthritis Research UK/United Kingdom
- P01 HL108795/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL108795/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AR064546/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR050250/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA060553/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI092490/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

