Bacterial chemoreceptors and chemoeffectors
- PMID: 25374297
- PMCID: PMC11113376
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-014-1770-5
Bacterial chemoreceptors and chemoeffectors
Abstract
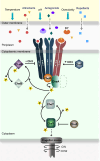
Bacteria use chemotaxis signaling pathways to sense environmental changes. Escherichia coli chemotaxis system represents an ideal model that illustrates fundamental principles of biological signaling processes. Chemoreceptors are crucial signaling proteins that mediate taxis toward a wide range of chemoeffectors. Recently, in deep study of the biochemical and structural features of chemoreceptors, the organization of higher-order clusters in native cells, and the signal transduction mechanisms related to the on-off signal output provides us with general insights to understand how chemotaxis performs high sensitivity, precise adaptation, signal amplification, and wide dynamic range. Along with the increasing knowledge, bacterial chemoreceptors can be engineered to sense novel chemoeffectors, which has extensive applications in therapeutics and industry. Here we mainly review recent advances in the E. coli chemotaxis system involving structure and organization of chemoreceptors, discovery, design, and characterization of chemoeffectors, and signal recognition and transduction mechanisms. Possible strategies for changing the specificity of bacterial chemoreceptors to sense novel chemoeffectors are also discussed.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hybrid Two-Component Sensors for Identification of Bacterial Chemoreceptor Function.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019 Oct 30;85(22):e01626-19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01626-19. Print 2019 Nov 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31492670 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial chemoreceptors: high-performance signaling in networked arrays.Trends Biochem Sci. 2008 Jan;33(1):9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2007.09.014. Epub 2007 Dec 31. Trends Biochem Sci. 2008. PMID: 18165013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A zipped-helix cap potentiates HAMP domain control of chemoreceptor signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Apr 10;115(15):E3519-E3528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1721554115. Epub 2018 Mar 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29581254 Free PMC article.
-
Chemotaxis of the Human Pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa to the Neurotransmitter Acetylcholine.mBio. 2022 Apr 26;13(2):e0345821. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03458-21. Epub 2022 Mar 7. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35254130 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transduction in bacterial chemotaxis.Bioessays. 2006 Jan;28(1):9-22. doi: 10.1002/bies.20343. Bioessays. 2006. PMID: 16369945 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring AI-2-mediated interspecies communications within rumen microbial communities.Microbiome. 2022 Oct 7;10(1):167. doi: 10.1186/s40168-022-01367-z. Microbiome. 2022. PMID: 36203182 Free PMC article.
-
The expression of many chemoreceptor genes depends on the cognate chemoeffector as well as on the growth medium and phase.Curr Genet. 2017 Jun;63(3):457-470. doi: 10.1007/s00294-016-0646-7. Epub 2016 Sep 8. Curr Genet. 2017. PMID: 27632030
-
Evidence for a Helix-Clutch Mechanism of Transmembrane Signaling in a Bacterial Chemoreceptor.J Mol Biol. 2016 Sep 25;428(19):3776-88. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.03.017. Epub 2016 Mar 24. J Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27019297 Free PMC article.
-
The Divergent Key Residues of Two Agrobacterium fabrum (tumefaciens) CheY Paralogs Play a Key Role in Distinguishing Their Functions.Microorganisms. 2021 May 24;9(6):1134. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9061134. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34074050 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori chemoreceptor TlpC mediates chemotaxis to lactate.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 26;7(1):14089. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14372-2. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29075010 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Krell T, Lacal J, Munoz-Martinez F, Reyes-Darias JA, Cadirci BH, Garcia-Fontana C, Ramos JL. Diversity at its best: bacterial taxis. Environ Microbiol. 2011;13:1115–1124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

