TRIFUNCTIONAL LIGANDS: A RADIOIODINATED HIGH AFFINITY ACYLATING ANTAGONIST FOR THE A1 ADENOSINE RECEPTOR
- PMID: 25374448
- PMCID: PMC4217529
TRIFUNCTIONAL LIGANDS: A RADIOIODINATED HIGH AFFINITY ACYLATING ANTAGONIST FOR THE A1 ADENOSINE RECEPTOR
Abstract
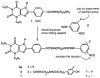
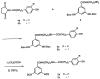
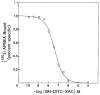
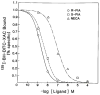
A new xanthine (adenosine antagonist) radioligand that binds covalently to A1-adenosine receptors was prepared and used as a receptor probe. BH-DITC-XAC was synthesized via a trifunctional aryl diisothiocyanate crosslinker. containing the p-hydroxyphenylpropionyl group for radioiodination. The xanthine competed against agonist or antagonist A1 receptor radioligands in bovine brain membranes with an IC50, of 40nM. 125I-BH-DITC-XAC, prepared directly by the chloramine T method and purified by HPLC. bound specifically to A1 receptors. This binding was inhibited in the presence of the adenosine agonists R-PIA, S-PIA. and NECA in a dose dependent manner and with the order of potency characteristic of bovine A1 receptors. Incubation of affinity purified bovine A1-receptors with 125I-BH-DITC-XAC (0.8 nM) for 2 hours resulted in the specific and clean labelling of a polypeptide band corresponding to MW 36,000, identical to that previously found for the A1 receptor.
Keywords: adenosine receptors; affinity labeling; radioiodination; xanthines.
Figures

References
-
- DeLean A, Munson PJ, Rodbard D. Simultaneous analysis of families of sigmoidal curves: application to bioassay, radioligand assay and physiological dose-response curves. Am J Physiol. 1978;235:E97–E106. - PubMed
-
- DeLean A, Hancock A, Lefkowitz RJ. Validation and statistical analysis of a computer modeling method for quantitative analysis of radioligand binding data for mixtures of pharmacological receptor subtypes. Mol Pharmacol. 1982;21:5–13. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
