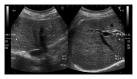
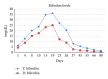
The possible efficacy of artichoke in fluconazole related hepatotoxicity
- PMID: 25374729
- PMCID: PMC4207603
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/697359
The possible efficacy of artichoke in fluconazole related hepatotoxicity
Abstract
Although fluconazole related hepatotoxicity (FRH) is rare, mortal acute hepatic necrosis and jaundice were reported in immunocompromised states such as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and bone marrow transplant (BMT). We present a case of a patient with multiple sclerosis who developed hepatotoxicity with the use of a single 150 mg fluconazole tablet for fungal vaginitis, 10 days after methylprednisolone pulse treatment. Our patient's alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels were decreased, 1200 U/L and 800 U/L, respectively, and bilirubin levels were consistent at 37 mg/dL. Artichoke which has anticholestatic and antioxidant properties was used by our patient. She consumed a 30 mg artichoke leaf extract tea 3 times a day. The bilirubin levels significantly declined at the end of the first week and all liver function tests were normalized within 2 months.
Figures
References
-
- Jacobson MA, Hanks DK, Ferrell LD. Fatal acute hepatic necrosis due to fluconazole. The American Journal of Medicine. 1994;96(2):188–190. - PubMed
-
- Mehmetçik G, Özdemirler G, Koçak-Toker N, Çevikbaş U, Uysal M. Effect of pretreatment with artichoke extract on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury and oxidative stress. Experimental and Toxicologic Pathology. 2008;60(6):475–480. - PubMed
-
- Björnsson E, Davidsdottir L. The long-term follow-up after idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury with jaundice. Journal of Hepatology. 2009;50(3):511–517. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources