Neurocognitive changes after lung transplantation
- PMID: 25375275
- PMCID: PMC4298983
- DOI: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201406-232OC
Neurocognitive changes after lung transplantation
Abstract
Rationale: Neurocognitive impairments are associated with reduced quality of life and may adversely affect medical compliance, but their prevalence after lung transplantation has not been extensively studied.
Objectives: To examine the frequency of neurocognitive impairment after lung transplantation and to examine perioperative factors affecting post-transplant neurocognitive function.
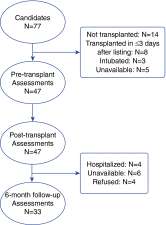
Measurements and main results: We performed serial assessments of neurocognitive function in a consecutive series of 47 subjects who received transplants between March 2013 and November 2013 (45% women; mean age, 53.5 ± 17.2 yr). Neurocognitive function was assessed using a composite measure including the Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS) total score and Trail Making Test parts A and B obtained before transplant, at hospital discharge, and 3 months after discharge. The presence of neurocognitive impairment was assessed using the Montreal Cognitive Assessment Battery (MoCA), and in-hospital delirium was assessed using the Confusion Assessment Method. Results demonstrated that neurocognitive performance initially worsened among non-cystic fibrosis patients and improved over follow-up (P = 0.002). Time effects were strongest on Trail Making Test part B (P < 0.001) and the RBANS (P = 0.054). Participants who exhibited delirium during their hospitalization showed poorer performance during follow-up assessments (P = 0.006). Examination of cognitive impairment rates demonstrated that 21 participants (45%) exhibited neurocognitive impairment (MoCA < 26) before lung transplant, whereas 27 (57%) participants exhibited impairment after transplantation, and 19 (57%) participants continued to neurocognitive impairment during a 3-month follow-up.
Conclusions: Neurocognitive impairments are prevalent among lung transplant candidates and appear to worsen in some patients after transplant. Delirium during hospitalization is associated with worse neurocognitive function after transplant among patients without cystic fibrosis.
Keywords: delirium; lung transplantation; neurocognitive performance.
Figures


Comment in
-
From research to clinical practice. Cognitive trajectory after lung transplantation.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2014 Dec;11(10):1604-5. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201410-487ED. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2014. PMID: 25549024 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Christie JD, Edwards LB, Kucheryavaya AY, Benden C, Dipchand AI, Dobbels F, Kirk R, Rahmel AO, Stehlik J, Hertz MI International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation. The registry of the international society for heart and lung transplantation: 29th adult lung and heart-lung transplant report-2012. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2012;31:1073–1086. - PubMed
-
- Valapour M, Paulson K, Smith JM, Hertz MI, Skeans MA, Heubner BM, Edwards LB, Snyder JJ, Israni AK, Kasiske BL. OPTN/SRTR 2011 annual data report: lung. Am J Transplant. 2013;13(Suppl 1):149–177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

