IKKα is required for the homeostasis of regulatory T cells and for the expansion of both regulatory and effector CD4 T cells
- PMID: 25376833
- PMCID: PMC4314223
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.14-259564
IKKα is required for the homeostasis of regulatory T cells and for the expansion of both regulatory and effector CD4 T cells
Abstract
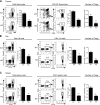
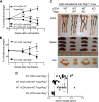
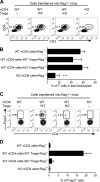
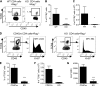
It was reported that TNF receptor type II signaling, which has the capacity to stimulate CD4+ forkhead box P3+ (Foxp3+) regulatory T cells (Tregs), activated the noncanonical NF-κB pathway in an IKKα-dependent manner. Therefore, we studied the role of IKKα in the homeostasis of Treg population. To this end, we generated a mouse strain with conditional knockout of IKKα in CD4 cells (Ikkα(f/f):CD4.Cre) that showed a >60% reduction in the number of Tregs in the thymus and peripheral lymphoid tissues, whereas the number of Foxp3- effector T cells (Teffs) remained at a normal level. The function of Tregs deficient in IKKα was examined using Rag1(-/-) mice cotransferred with naive CD4 cells (nCD4s). Although wild-type (WT) Tregs inhibited colitis induced by transfer of WT nCD4s, IKKα-deficient Tregs failed to do so, which was associated with their inability to reconstitute Rag1(-/-) mice. Furthermore, nCD4s deficient in IKKα also failed to reconstitute Rag1(-/-) mice and were defective in proliferative responses in vitro and in vivo. Thus, our study reveals a novel role of IKKα in the maintenance of a normal Treg population and in the control of expansion of CD4 T cells. These properties of IKKα may be exploited as therapeutic strategies in the treatment of major human diseases.
Keywords: Foxp3; colitis; lymphopenic mouse; proliferation.
© FASEB.
Figures


References
-
- Kaech S. M., Wherry E. J., Ahmed R. (2002) Effector and memory T-cell differentiation: implications for vaccine development. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2, 251–262 - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi S., Yamaguchi T., Nomura T., Ono M. (2008) Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell 133, 775–787 - PubMed
-
- Zou W. (2006) Regulatory T cells, tumour immunity and immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6, 295–307 - PubMed
-
- Dev A., Iyer S., Razani B., Cheng G. (2011) NF-κB and innate immunity. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 349, 115–143 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

