Perylene-diimide-based nanoparticles as highly efficient photoacoustic agents for deep brain tumor imaging in living mice
- PMID: 25376906
- PMCID: PMC4347809
- DOI: 10.1002/adma.201402972
Perylene-diimide-based nanoparticles as highly efficient photoacoustic agents for deep brain tumor imaging in living mice
Abstract
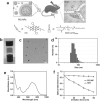
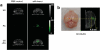
In order to promote preclinical and clinical applications of photoacoustic imaging, novel photoacoustic contrast agents are highly desired for molecular imaging of diseases, especially for deep tumor imaging. Here, perylene-3,4,9,10-tetracarboxylic diiimide-based near-infrared-absorptive organic nanoparticles are reported as an efficient agent for photoacoustic imaging of deep brain tumors in living mice with enhanced permeability and retention effect.
Keywords: Perylene-3,4,9,10-tetracarboxylic diimide nanoparticles; brain tumor; deep tumor imaging; near-infrared-absorption; photoacoustic imaging.
© 2014 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures

Comment in
-
Highlights from the latest articles in nanomedicine for deep tumor imaging and phototherapy.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2015;10(11):1681-3. doi: 10.2217/nnm.15.63. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2015. PMID: 26080692 No abstract available.
References
-
- Song KH, Kim C, Cobley CM, Xia Y, Wang LV. Nano Lett. 2009;9:183. - PMC - PubMed
- Jokerst JV, Thangaraj M, Kempen PJ, Sinclair R, Gambhir SS. ACS Nano. 2012;6:5920. - PMC - PubMed
- Cheng K, Kothapalli SR, Liu H, Koh AL, Jokerst JV, Jiang H, Yang M, Li J, Levi J, Wu JC, Gambhir SS, Cheng Z. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014;136:3560. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

