Effect of ketoconazole and diltiazem on the pharmacokinetics of apixaban, an oral direct factor Xa inhibitor
- PMID: 25377242
- PMCID: PMC4415720
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.12541
Effect of ketoconazole and diltiazem on the pharmacokinetics of apixaban, an oral direct factor Xa inhibitor
Abstract
Aim: Apixaban is an orally active inhibitor of coagulation factor Xa and is eliminated by multiple pathways, including renal and non-renal elimination. Non-renal elimination pathways consist of metabolism by cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes, primarily CYP3A4, as well as direct intestinal excretion. Two single sequence studies evaluated the effect of ketoconazole (a strong dual inhibitor of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein [P-gp]) and diltiazem (a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor and a P-gp inhibitor) on apixaban pharmacokinetics in healthy subjects.
Method: In the ketoconazole study, 18 subjects received apixaban 10 mg on days 1 and 7, and ketoconazole 400 mg once daily on days 4-9. In the diltiazem study, 18 subjects received apixaban 10 mg on days 1 and 11 and diltiazem 360 mg once daily on days 4-13.
Results: Apixaban maximum plasma concentration and area under the plasma concentration-time curve extrapolated to infinity increased by 62% (90% confidence interval [CI], 47, 78%) and 99% (90% CI, 81, 118%), respectively, with co-administration of ketoconazole, and by 31% (90% CI, 16, 49%) and 40% (90% CI, 23, 59%), respectively, with diltiazem.
Conclusion: A 2-fold and 1.4-fold increase in apixaban exposure was observed with co-administration of ketoconazole and diltiazem, respectively.
Keywords: CYP3A4 inhibitors; P-glycoprotein inhibitors; anticoagulants; apixaban; drug-drug interactions.
© 2014 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

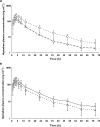
 , apixaban 10 mg (n = 19);
, apixaban 10 mg (n = 19);  , apixaban + ketoconazole 400 mg once daily (n = 18) and (B) diltiazem,
, apixaban + ketoconazole 400 mg once daily (n = 18) and (B) diltiazem,  , apixaban 10 mg (n = 18);
, apixaban 10 mg (n = 18);  , apixaban 10 mg + diltiazem 360 mg once daily (n = 18)
, apixaban 10 mg + diltiazem 360 mg once daily (n = 18)References
-
- Pinto DJ, Orwat MJ, Koch S, Rossi KA, Alexander RS, Smallwood A, Wong PC, Rendina AR, Luettgen JM, Knabb RM, He K, Xin B, Wexler RR, Lam PY. Discovery of 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-7-oxo-6-(4-(2-oxopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridine-3-carboxamide (apixaban, BMS-562247), a highly potent, selective, efficacious, and orally bioavailable inhibitor of blood coagulation factor Xa. J Med Chem. 2007;50:5339–5356. - PubMed
-
- Wong PC, Crain EJ, Xin B, Wexler RR, Lam PY, Pinto DJ, Luettgen JM, Knabb RM. Apixaban, an oral, direct and highly selective factor Xa inhibitor: in vitro, antithrombotic and antihemostatic studies. J Thromb Haemost. 2008;6:820–829. - PubMed
-
- Connolly SJ, Eikelboom J, Joyner C, Diener HC, Hart R, Golitsyn S, Flaker G, Avezum A, Hohnloser SH, Diaz R, Talajic M, Zhu J, Pais P, Budaj A, Parkhomenko A, Jansky P, Commerford P, Tan RS, Sim KH, Lewis BS, Van Mieghem W, Lip GY, Kim JH, Lanas-Zanetti F, Gonzalez-Hermosillo A, Dans AL, Munawar M, O'Donnell M, Lawrence J, Lewis G, Afzal R, Yusuf S. Apixaban in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:806–817. - PubMed
-
- Granger CB, Alexander JH, McMurray JJ, Lopes RD, Hylek E, Hanna M, Al-Khalidi HR, Ansell J, Atar D, Avezum A, Bahit MC, Diaz R, Easton JD, Ezekowitz JA, Flaker G, Garcia D, Geraldes M, Gersh BJ, Golitsyn S, Goto S, Hermosillo AG, Hohnloser S, Horowitz J, Mohan P, Jansky P, Lewis BS, Lopez-Sendon J, Pais P, Parkhomenko A, Verheugt F, Zhu J, Wallentin L. Apixaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:981–992. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

