Effects of Repeated Intravenous Administration of Dextrans,Water-soluble Macromolecules, in Rats
- PMID: 25378808
- PMCID: PMC4217235
- DOI: 10.1293/tox.2013-0067
Effects of Repeated Intravenous Administration of Dextrans,Water-soluble Macromolecules, in Rats
Erratum in
-
Errata (Printer's correction).J Toxicol Pathol. 2016 Jan;29(1):74. Epub 2016 Feb 17. J Toxicol Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26989306 Free PMC article.
Abstract
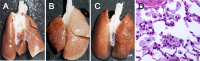
We investigated the influence of repeated intravenous administration of dextrans (DEXs) to rats. Seven-week-old Sprague Dawley rats (6 males/group) were given intravenously 10% saline solutions of dextrans (DEXs), 40 kDa or 200-300 kDa, at a dose level of 5 mL/kg/day for 28 days and they were examined histopathologically. Another group (3 males/group) was administered saline in a similar manner and served as the control. Histopathological changes indicating accumulation of DEXs in the mononuclear phagocyte system (MPS) and the liver were noted in the treated groups. The incidence and severity of the findings were molecular weight-dependent, except for the lungs. These results are considered useful in interpreting data from preclinical studies, in which DEXs or their derivatives are administered as test or control substances.
Keywords: intravenous administration; macromolecular substances; mononuclear phagocyte system.
Figures


References
-
- Mehvar R. Dextrans for targeted and sustained delivery of therapeutic and imaging agents. J Control Release. 69: 1–25. 2000. - PubMed
-
- Dhaneshwar SS, Kandpal M, Gairola N, and Kadam SS. Dextran: A promising macromolecular drug carrier. Indian J Pharm Sci. 68: 705–714. 2006.
-
- Burns DL, Mascioli EA, and Bistrian BR. Parenteral iron dextran therapy: a review. Nutrition. 11: 163–168. 1995. - PubMed
-
- Larsen C. Dextran prodrugs — structure and stability in relation to therapeutic activity. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 3: 103–154. 1989.
-
- Mehvar R, Robinson MA, and Reynolds JM. Molecular weight dependent tissue accumulation of dextrans: in vivo studies in rats. J Pharm Sci. 83: 1495–1499. 1994. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
