Enhanced breast cancer therapy with nsPEFs and low concentrations of gemcitabine
- PMID: 25379013
- PMCID: PMC4209047
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-014-0098-4
Enhanced breast cancer therapy with nsPEFs and low concentrations of gemcitabine
Abstract
Background: Chemotherapy either before or after surgery is a common breast cancer treatment. Long-term, high dose treatments with chemotherapeutic drugs often result in undesirable side effects, frequent recurrences and resistances to therapy.
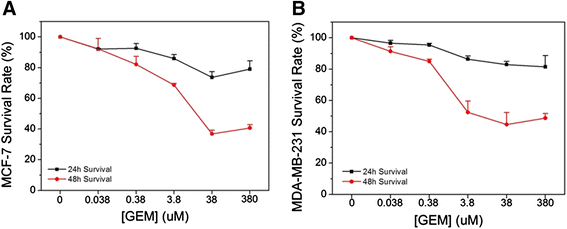
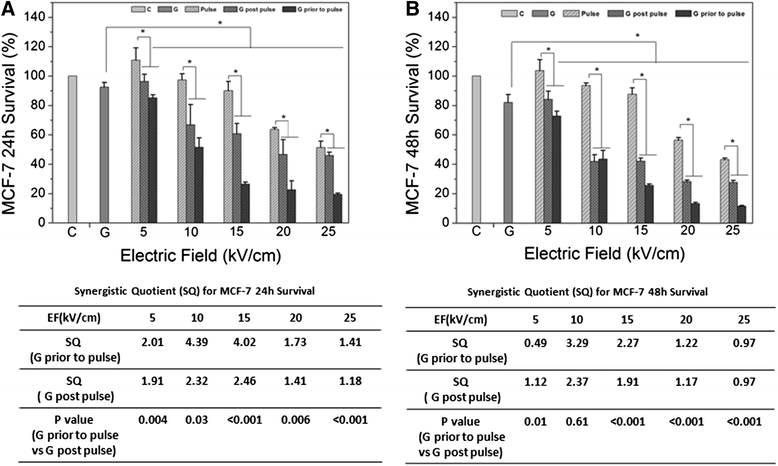
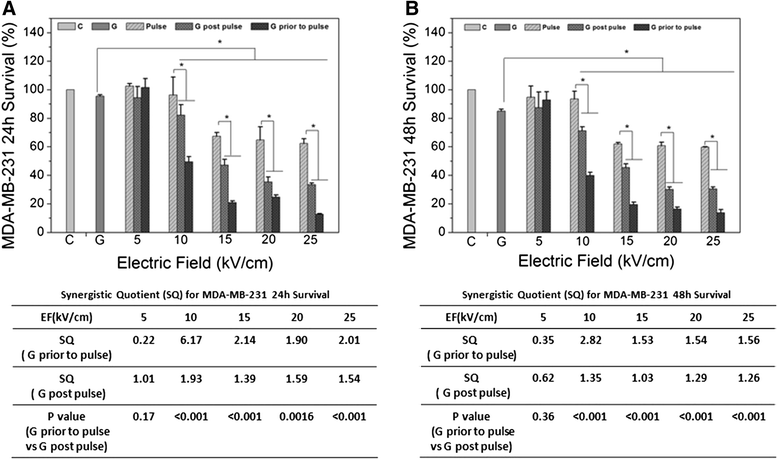
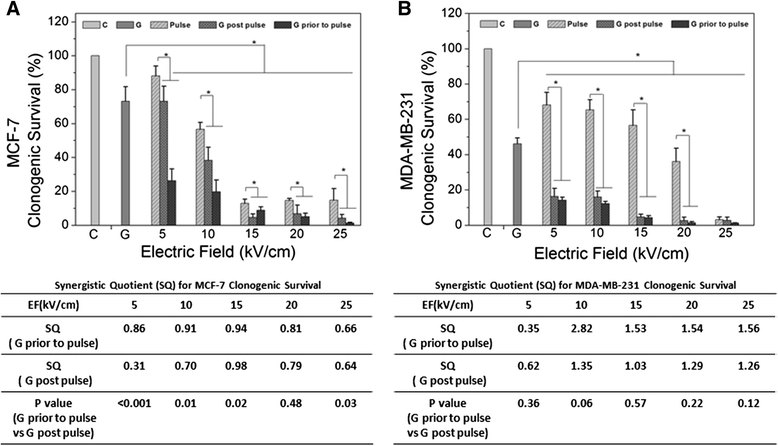
Methods: The anti-cancer drug, gemcitabine (GEM) was used in combination with pulse power technology with nanosecond pulsed electric fields (nsPEFs) for treatment of human breast cancer cells in vitro. Two strategies include sensitizing mammary tumor cells with GEM before nsPEF treatment or sensitizing cells with nsPEFs before GEM treatment. Breast cancer cell lines MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 were treated with 250 65 ns-duration pulses and electric fields of 15, 20 or 25 kV/cm before or after treatment with 0.38 μM GEM.
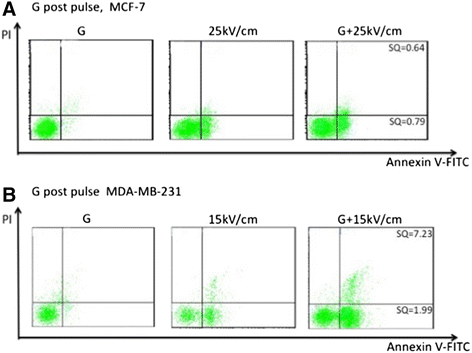
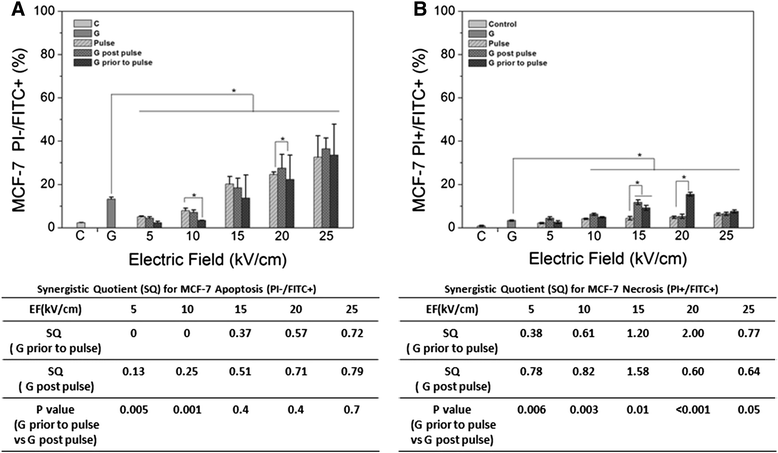
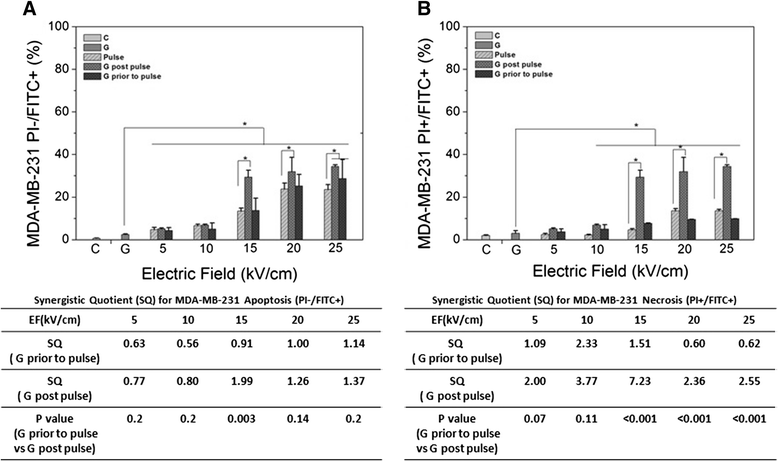
Results: Both cell lines exhibited robust synergism for loss of cell viability 24 h and 48 h after treatment; treatment with GEM before nsPEFs was the preferred order. In clonogenic assays, only MDA-MB-231 cells showed synergism; again GEM before nsPEFs was the preferred order. In apoptosis/necrosis assays with Annexin-V-FITC/propidium iodide 2 h after treatment, both cell lines exhibited apoptosis as a major cell death mechanism, but only MDA-MB-231 cells exhibited modest synergism. However, unlike viability assays, nsPEF treatment before GEM was preferred. MDA-MB-231 cells exhibited much greater levels of necrosis then in MCF-7 cells, which were very low. Synergy was robust and greater when nsPEF treatment was before GEM.
Conclusions: Combination treatments with low GEM concentrations and modest nsPEFs provide enhanced cytotoxicity in two breast cancer cell lines. The treatment order is flexible, although long-term survival and short-term cell death analyses indicated different treatment order preferences. Based on synergism, apoptosis mechanisms for both agents were more similar in MCF-7 than in MDA-MB-231 cells. In contrast, necrosis mechanisms for the two agents were distinctly different in MDA-MB-231, but too low to reliably evaluate in MCF-7 cells. While disease mechanisms in the two cell lines are different based on the differential synergistic response to treatments, combination treatment with GEM and nsPEFs should provide an advantageous therapy for breast cancer ablation in vivo.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Breast cancer; Clonogenics; Gemcitabine; MCF-7; MDA-MB-231; Nanosecond pulsed electric fields (nsPEFs); Necrosis (necroptosis); Non-thermal; Synergism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synergistic effects of nanosecond pulsed electric fields combined with low concentration of gemcitabine on human oral squamous cell carcinoma in vitro.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43213. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043213. Epub 2012 Aug 23. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22927951 Free PMC article.
-
Nanosecond pulsed electric fields (nsPEFs) impact and enhanced Photofrin II(®) delivery in photodynamic reaction in cancer and normal cells.Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2015 Dec;12(4):621-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2015.11.002. Epub 2015 Nov 10. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2015. PMID: 26563460
-
Nanosecond pulsed electric fields induce poly(ADP-ribose) formation and non-apoptotic cell death in HeLa S3 cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Aug 30;438(3):557-62. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.07.083. Epub 2013 Jul 27. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23899527
-
Nanosecond pulsed electric field ablates rabbit VX2 liver tumors in a non-thermal manner.PLoS One. 2023 Mar 15;18(3):e0273754. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273754. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36920938 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of Conventional Drugs with Biocompounds Derived from Cinnamic Acid: A Promising Option for Breast Cancer Therapy.Biomedicines. 2023 Jan 19;11(2):275. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020275. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36830811 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dual-function of Baicalin in nsPEFs-treated Hepatocytes and Hepatocellular Carcinoma cells for Different Death Pathway and Mitochondrial Response.Int J Med Sci. 2019 Sep 7;16(9):1271-1282. doi: 10.7150/ijms.34876. eCollection 2019. Int J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31588193 Free PMC article.
-
Gemcitabine‑fucoxanthin combination in human pancreatic cancer cells.Biomed Rep. 2023 Jun 1;19(1):46. doi: 10.3892/br.2023.1629. eCollection 2023 Jul. Biomed Rep. 2023. PMID: 37324167 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Cellular Doxorubicin Uptake via Delayed Exposure Following Nanosecond Pulsed Electric Field Treatment: An In Vitro Study.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jun 24;16(7):851. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16070851. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39065548 Free PMC article.
-
Necroptosis in tumorigenesis, activation of anti-tumor immunity, and cancer therapy.Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 30;7(35):57391-57413. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10548. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27429198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of Anti-tumor Immune Response by Ablation of HCC with Nanosecond Pulsed Electric Field.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2018 Mar 28;6(1):85-88. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2017.00042. Epub 2017 Oct 27. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 29577034 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tilanus-Linthorst MM, Obdeijn IM, Hop WC, Causer PA, Leach MO, Warner E, Pointon L, Hill K, Klijn JG, Warren RM, Gilbert FJ. BRCA1 mutation and young age predict fast breast cancer growth in the Dutch, United Kingdom, and Canadian magnetic resonance imaging screening trials. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:7357–7362. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0689. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

