Modulation of rotation-induced lift force for cell filtration in a low aspect ratio microchannel
- PMID: 25379097
- PMCID: PMC4189218
- DOI: 10.1063/1.4891599
Modulation of rotation-induced lift force for cell filtration in a low aspect ratio microchannel
Abstract
Cell filtration is a critical step in sample preparation in many bioapplications. Herein, we report on a simple, filter-free, microfluidic platform based on hydrodynamic inertial migration. Our approach builds on the concept of two-stage inertial migration which permits precise prediction of microparticle position within the microchannel. Our design manipulates equilibrium positions of larger microparticles by modulating rotation-induced lift force in a low aspect ratio microchannel. Here, we demonstrate filtration of microparticles with extreme efficiency (>99%). Using multiple prostate cell lines (LNCaP and human prostate epithelial tumor cells), we show filtration from spiked blood, with 3-fold concentration and >83% viability. Results of a proliferation assay show normal cell division and suggest no negative effects on intrinsic properties. Considering the planar low-aspect-ratio structure and predictable focusing, we envision promising applications and easy integration with existing lab-on-a-chip systems.
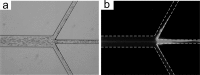
Figures






References
-
- Khoshmanesh K., Baratchi S., Tovar-Lopez F. J., Nahavandi S., Wlodkowic D., Mitchell A., and Kalantar-zadeh K., “ On-chip separation of Lactobacillus bacteria from yeasts using dielectrophoresis,” Microfluid. Nanofluid. 12, 597–606 (2012). 10.1007/s10404-011-0900-8 - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
