Deciphering the role of phytoalexins in plant-microorganism interactions and human health
- PMID: 25379642
- PMCID: PMC6271817
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules191118033
Deciphering the role of phytoalexins in plant-microorganism interactions and human health
Abstract
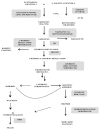
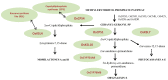
Phytoalexins are low molecular weight antimicrobial compounds that are produced by plants as a response to biotic and abiotic stresses. As such they take part in an intricate defense system which enables plants to control invading microorganisms. In this review we present the key features of this diverse group of molecules, namely their chemical structures, biosynthesis, regulatory mechanisms, biological activities, metabolism and molecular engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Müller K.O., Börger H. Experimentelle Untersuchungen über die Phytophthora Resistenz der Kartoffel. Arb. Biol. Reichsanst. Land Forstwirtsch. 1940;23:189–231.
-
- Deverall B.J. Introduction. In: Bailey J.A., Mansfield J.W., editors. Phytoalexins. Blackie; Glasgow/London, UK: 1982. pp. 1–20.
-
- Ingham J.L. Phytoalexins from the Leguminosae. In: Bailey J.A., Mansfield J.W., editors. Phytoalexins. Blackie; Glasgow/London, UK: 1982. pp. 21–80.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

