Musashi proteins are post-transcriptional regulators of the epithelial-luminal cell state
- PMID: 25380226
- PMCID: PMC4381951
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.03915
Musashi proteins are post-transcriptional regulators of the epithelial-luminal cell state
Abstract
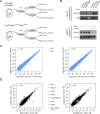
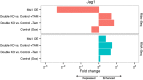
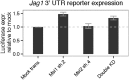
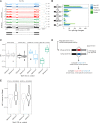
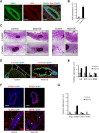
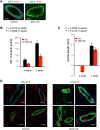
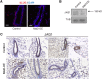
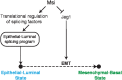
The conserved Musashi (Msi) family of RNA binding proteins are expressed in stem/progenitor and cancer cells, but generally absent from differentiated cells, consistent with a role in cell state regulation. We found that Msi genes are rarely mutated but frequently overexpressed in human cancers and are associated with an epithelial-luminal cell state. Using ribosome profiling and RNA-seq analysis, we found that Msi proteins regulate translation of genes implicated in epithelial cell biology and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and promote an epithelial splicing pattern. Overexpression of Msi proteins inhibited the translation of Jagged1, a factor required for EMT, and repressed EMT in cell culture and in mammary gland in vivo. Knockdown of Msis in epithelial cancer cells promoted loss of epithelial identity. Our results show that mammalian Msi proteins contribute to an epithelial gene expression program in neural and mammary cell types.
Keywords: alternative splicing; cancer genomics; epithelial–mesenchymal transition; evolutionary biology; genomics; human; human biology; medicine; mouse; translational regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
EMA: Reviewing Editor,
The other authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
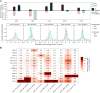

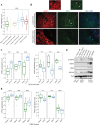
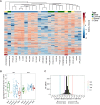
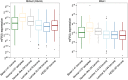



References
-
- Chakrabarti R, Hwang J, Andres Blanco M, Wei Y, Lukačišin M, Romano RA, Smalley K, Liu S, Yang Q, Ibrahim T, Mercatali L, Amadori D, Haffty BG, Sinha S, Kang Y. Elf5 inhibits the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in mammary gland development and breast cancer metastasis by transcriptionally repressing Snail2. Nature Cell Biology. 2012;14:1212–1222. doi: 10.1038/ncb2607. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- T32 GM007287/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA084198/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01-CA184897/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM096193/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-GM096193/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA184897/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HD045022/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA084198/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD045022/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA084198/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-GM085319/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM085319/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

