Astrogliosis
- PMID: 25380660
- PMCID: PMC4315924
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a020420
Astrogliosis
Abstract
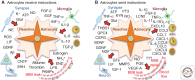
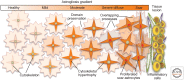
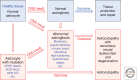
In addition to their many functions in the healthy central nervous system (CNS), astrocytes respond to CNS damage and disease through a process called astrogliosis. For many decades, astrogliosis was sparsely studied and enigmatic. This article examines recent evidence supporting a definition of astrogliosis as a spectrum of heterogeneous potential changes in astrocytes that occur in a context-specific manner as determined by diverse signaling events that vary with the nature and severity of different CNS insults. Astrogliosis is associated with essential beneficial functions, but under specific circumstances can lead to harmful effects. Potential dysfunctions of astrocytes and astrogliosis are being identified that can contribute to, or be primary causes of, CNS disorders, leading to the notion of astrocytopathies. A conceptual framework is presented that allows consideration of normally occurring and dysfunctional astrogliosis and their different roles in CNS disorders.
Copyright © 2015 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bardehle S, Kruger M, Buggenthin F, Schwausch J, Ninkovic J, Clevers H, Snippert HJ, Theis FJ, Meyer-Luehmann M, Bechmann I, et al. 2013. Live imaging of astrocyte responses to acute injury reveals selective juxtavascular proliferation. Nat Neurosci 16: 580–586. - PubMed
-
- Barnabe-Heider F, Goritz C, Sabelstrom H, Takebayashi H, Pfrieger FW, Meletis K, Frisen J 2010. Origin of new glial cells in intact and injured adult spinal cord. Cell Stem Cell 7: 470–482. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
