Genome-wide association study of Arabidopsis thaliana leaf microbial community
- PMID: 25382143
- PMCID: PMC4232226
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms6320
Genome-wide association study of Arabidopsis thaliana leaf microbial community
Abstract
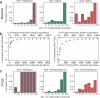
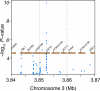
Identifying the factors that influence the outcome of host-microbial interactions is critical to protecting biodiversity, minimizing agricultural losses and improving human health. A few genes that determine symbiosis or resistance to infectious disease have been identified in model species, but a comprehensive examination of how a host genotype influences the structure of its microbial community is lacking. Here we report the results of a field experiment with the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana to identify the fungi and bacteria that colonize its leaves and the host loci that influence the microbe numbers. The composition of this community differs among accessions of A. thaliana. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) suggest that plant loci responsible for defense and cell wall integrity affect variation in this community. Furthermore, species richness in the bacterial community is shaped by host genetic variation, notably at loci that also influence the reproduction of viruses, trichome branching and morphogenesis.
Figures

References
-
- Fromin N, Achouak W, Thiéry JM, Heulin T. The genotypic diversity of Pseudomonas brassicacearum populations isolated from roots of Arabidopsis thaliana: influence of plant genotype. FEMS Microbiology Ecology. 2001;37:21–29.
-
- Bulgarelli D, et al. Revealing structure and assembly cues for Arabidopsis root-inhabiting bacterial microbiota. Nature. 2012;488:91–95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

