Pressure-induced metallization of dense (H₂S)₂H₂ with high-Tc superconductivity
- PMID: 25382349
- PMCID: PMC4225546
- DOI: 10.1038/srep06968
Pressure-induced metallization of dense (H₂S)₂H₂ with high-Tc superconductivity
Abstract
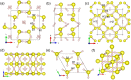
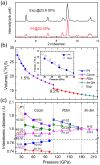
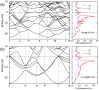
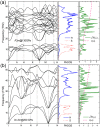
The high pressure structures, metallization, and superconductivity of recently synthesized H2-containing compounds (H2S)2H2 are elucidated by ab initio calculations. The ordered crystal structure with P1 symmetry is determined, supported by the good agreement between theoretical and experimental X-ray diffraction data, equation of states, and Raman spectra. The Cccm structure is favorable with partial hydrogen bond symmetrization above 37 GPa. Upon further compression, H2 molecules disappear and two intriguing metallic structures with R3m and Im-3m symmetries are reconstructive above 111 and 180 GPa, respectively. The predicted metallization pressure is 111 GPa, which is approximately one-third of the currently suggested metallization pressure of bulk molecular hydrogen. Application of the Allen-Dynes-modified McMillan equation for the Im-3m structure yields high Tc values of 191 K to 204 K at 200 GPa, which is among the highest values reported for H2-rich van der Waals compounds and MH3 type hydride thus far.
Figures

References
-
- Vos W. L., Finger L. W., Hemley R. J. & Mao H.-K. Novel H2-H2O clathrates at high pressures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 3150–3153 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Strobel T. A., Ganesh P., Somayazulu M., Kent P. R. C. & Hemley R. J. Novel Cooperative Interactions and Structural Ordering in H2S-H2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 255503 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Somayazulu M. S., Finger L. W., Hemley R. J. & Mao H. K. High-Pressure Compounds in Methane-Hydrogen Mixtures. Science 271, 1400–1402 (1996).
-
- Strobel T. A., Somayazulu M. & Hemley R. J. Novel Pressure-Induced Interactions in Silane-Hydrogen. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 065701–065704 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

