Indian jujuba seed powder as an eco-friendly and a low-cost biosorbent for removal of acid blue 25 from aqueous solution
- PMID: 25383360
- PMCID: PMC4213431
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/184058
Indian jujuba seed powder as an eco-friendly and a low-cost biosorbent for removal of acid blue 25 from aqueous solution
Abstract
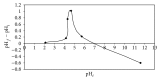
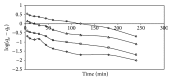
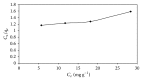
Indian jujuba seed powder (IJSP) has been investigated as a low-cost and an eco-friendly biosorbent, prepared for the removal of Acid Blue 25 (AB25) from aqueous solution. The prepared biomaterial was characterized by using FTIR and scanning electron microscopic studies. The effect of operation variables, such as IJSP dosage, contact time, concentration, pH, and temperature on the removal of AB25 was investigated, using batch biosorption technique. Removal efficiency increased with increase of IJSP dosage but decreased with increase of temperature. The equilibrium data were analyzed by the Langmuir and the Freundlich isotherm models. The data fitted well with the Langmuir model with a maximum biosorption capacity of 54.95 mg g(-1). The pseudo-second-order kinetics was the best for the biosorption of AB25 by IJSP, with good correlation. Thermodynamic parameters such as standard free energy change (ΔG(0)), standard enthalpy changes (ΔH(0)), and standard entropy changes (ΔS(0)) were analyzed. The removal of AB25 from aqueous solution by IJSP was a spontaneous and exothermic adsorption process. The results suggest that IJSP is a potential low-cost and an eco-friendly biosorbent for the AB25 removal from synthetic AB25 wastewater.
Figures











References
-
- Moussavi G., Khosravi R. The removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto pistachio hull waste. Chemical Engineering Research and Design. 2011;89(10):2182–2189. doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2010.11.024. - DOI
-
- Anbia M., Hariri S. A. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution using nanoporous SBA-3. Desalination. 2010;261(1-2):61–66. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2010.05.030. - DOI
-
- Hameed B. H., Hakimi H. Utilization of durian (Durio zibethinus Murray) peel as low cost sorbent for the removal of acid dye from aqueous solutions. Biochemical Engineering Journal. 2008;39(2):338–343. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2007.10.005. - DOI
-
- Jaikumar V., Sathish Kumar K., Gnana Praksh D. Biosorption of acid dyes using spent brewery grains: characterization and modeling. International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering. 2009;7:115–125.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

