The neural representation of taste quality at the periphery
- PMID: 25383521
- PMCID: PMC4297533
- DOI: 10.1038/nature13873
The neural representation of taste quality at the periphery
Abstract
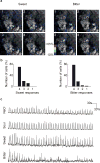
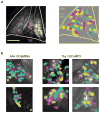
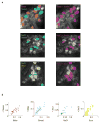
The mammalian taste system is responsible for sensing and responding to the five basic taste qualities: sweet, sour, bitter, salty and umami. Previously, we showed that each taste is detected by dedicated taste receptor cells (TRCs) on the tongue and palate epithelium. To understand how TRCs transmit information to higher neural centres, we examined the tuning properties of large ensembles of neurons in the first neural station of the gustatory system. Here, we generated and characterized a collection of transgenic mice expressing a genetically encoded calcium indicator in central and peripheral neurons, and used a gradient refractive index microendoscope combined with high-resolution two-photon microscopy to image taste responses from ganglion neurons buried deep at the base of the brain. Our results reveal fine selectivity in the taste preference of ganglion neurons; demonstrate a strong match between TRCs in the tongue and the principal neural afferents relaying taste information to the brain; and expose the highly specific transfer of taste information between taste cells and the central nervous system.
Figures


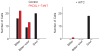



Comment in
-
Sensory processing: Geniculate ganglion neurons have individual tastes.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2015 Jan;16(1):4. doi: 10.1038/nrn3883. Epub 2014 Nov 26. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25423897 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

