A mass spectrometry assay to simultaneously analyze ROS1 and RET fusion gene expression in non-small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 25384172
- PMCID: PMC4304926
- DOI: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000337
A mass spectrometry assay to simultaneously analyze ROS1 and RET fusion gene expression in non-small-cell lung cancer
Abstract
Introduction: ROS1 and RET gene fusions were recently discovered in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) as potential therapeutic targets with small-molecule kinase inhibitors. The conventional screening methods of these fusions are time-consuming and require samples of high quality and quantity. Here, we describe a novel and efficient method by coupling the power of multiplexing polymerase chain reaction and the sensitivity of mass spectrometry.
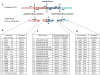
Methods: The multiplex mass spectrometry platform simultaneously tests samples for the expression of nine ROS1 and six RET fusion genes. The assay incorporates detection of wild-type exon junctions immediately upstream and downstream of the fusion junction to exclude false-negative results. To flag false-positives, the system also comprises two independent assays for each fusion gene junction.
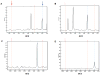
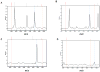
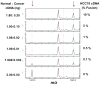
Results: The characteristic mass spectrometric peaks of the gene fusions were obtained using engineered plasmid constructs. Specific assays targeting the wild-type gene exon junctions were validated using complimentary DNA from lung tissue of healthy individuals. The system was further validated using complimentary DNA derived from NSCLC cell lines that express endogenous fusion genes. The expressed ROS1-SLC34A2 and CCDC6-RET gene fusions from the NSCLC cell lines HCC78 and LC-2/ad, respectively, were accurately detected by the novel assay. The assay is extremely sensitive, capable of detecting an event in test specimens containing 0.5% positive tumors.
Conclusion: The novel multiplexed assay is robustly capable of detecting 15 different clinically relevant RET and ROS1 fusion variants. The benefits of this detection method include exceptionally low sample input, high cost efficiency, flexibility, and rapid turnover.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
A single-tube multiplexed assay for detecting ALK, ROS1, and RET fusions in lung cancer.J Mol Diagn. 2014 Mar;16(2):229-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2013.11.007. Epub 2014 Jan 10. J Mol Diagn. 2014. PMID: 24418728
-
Identification of ALK, ROS1, and RET Fusions by a Multiplexed mRNA-Based Assay in Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Samples from Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients.Clin Chem. 2017 Mar;63(3):751-760. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2016.265314. Epub 2017 Jan 10. Clin Chem. 2017. PMID: 28073897
-
Multicenter evaluation of an automated, multiplex, RNA-based molecular assay for detection of ALK, ROS1, RET fusions and MET exon 14 skipping in NSCLC.Virchows Arch. 2024 Apr;484(4):677-686. doi: 10.1007/s00428-024-03778-9. Epub 2024 Mar 16. Virchows Arch. 2024. PMID: 38492039 Free PMC article.
-
Novel targets in non-small cell lung cancer: ROS1 and RET fusions.Oncologist. 2013;18(7):865-75. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2013-0095. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Oncologist. 2013. PMID: 23814043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ROS1 protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of ROS1 fusion protein-driven non-small cell lung cancers.Pharmacol Res. 2017 Jul;121:202-212. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.04.022. Epub 2017 Apr 30. Pharmacol Res. 2017. PMID: 28465216 Review.
Cited by
-
Profiling the Mutational Landscape in Known Driver Genes and Novel Genes in African American Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients.Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jul 15;25(14):4300-4308. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-2439. Epub 2019 Apr 12. Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30979741 Free PMC article.
-
Analytic and Clinical Validation of a Pan-Cancer NGS Liquid Biopsy Test for the Detection of Copy Number Amplifications, Fusions and Exon Skipping Variants.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Mar 17;12(3):729. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12030729. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35328282 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a high-throughput and sensitive assay of fusion genes in lung cancer by array-based MALDI-TOFMS.RSC Adv. 2018 Aug 6;8(49):27935-27945. doi: 10.1039/c8ra05165h. eCollection 2018 Aug 2. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35548167 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rikova K, Guo A, Zeng Q, et al. Global survey of phosphotyrosine signaling identifies oncogenic kinases in lung cancer. Cell. 2007;131:1190–203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

