Lycopene attenuates colistin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice via activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway
- PMID: 25385104
- PMCID: PMC4291401
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.03925-14
Lycopene attenuates colistin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice via activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway
Abstract
Nephrotoxicity is the major dose-limiting factor for the clinical use of colistin against multidrug-resistant (MDR) Gram-negative bacteria. This study aimed to investigate the protective effect of lycopene on colistin-induced nephrotoxicity in a mouse model. Fifty mice were randomly divided into 5 groups: the control group (saline solution), the lycopene group (20 mg/kg of body weight/day administered orally), the colistin group (15 mg/kg/day administered intravenously), the colistin (15 mg/kg/day) plus lycopene (5 mg/kg/day) group, and the colistin (15 mg/kg/day) plus lycopene (20 mg/kg/day) group; all mice were treated for 7 days. At 12 h after the last dose, blood was collected for measurements of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and serum creatinine levels. The kidney tissue samples were obtained for examination of biomarkers of oxidative stress and apoptosis, histopathological assessment, and quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis. Colistin treatment significantly increased concentrations of BUN and serum creatinine, tubular apoptosis/necrosis, lipid peroxidation, and heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1) activity, while the treatment decreased the levels of endogenous antioxidant biomarkers glutathione (GSH), catalase (CAT), and superoxide dismutase (SOD). Notably, the changes in the levels of all biomarkers were attenuated in the kidneys of mice treated with colistin by lycopene (5 or 20 mg/kg). Lycopene treatment, especially in the colistin plus lycopene (20 mg/kg) group, significantly downregulated the expression of NF-κB mRNA (P < 0.01) but upregulated the expression of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and HO-1 mRNA (both P < 0.01) in the kidney compared with the results seen with the colistin group. Our data demonstrated that coadministration of 20 mg/kg/day lycopene can protect against colistin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice. This effect may be attributed to the antioxidative property of lycopene and its ability to activate the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

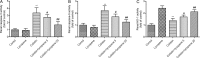

Similar articles
-
Baicalein acts as a nephroprotectant that ameliorates colistin-induced nephrotoxicity by activating the antioxidant defence mechanism of the kidneys and down-regulating the inflammatory response.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017 Sep 1;72(9):2562-2569. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkx185. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28859441 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of 6-hydroxy-1-methylindole-3-acetonitrile on cisplatin-induced oxidative nephrotoxicity via Nrf2 inactivation.Food Chem Toxicol. 2013 Dec;62:159-66. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.08.039. Epub 2013 Aug 26. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23989062
-
Beneficial effect of lycopene on anti-diabetic nephropathy through diminishing inflammatory response and oxidative stress.Food Funct. 2015 Apr;6(4):1150-6. doi: 10.1039/c5fo00004a. Food Funct. 2015. PMID: 25689917
-
A review on colistin nephrotoxicity.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2015 Jul;71(7):801-10. doi: 10.1007/s00228-015-1865-4. Epub 2015 May 27. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26008213 Review.
-
Prevention of colistin induced nephrotoxicity: a review of preclinical and clinical data.Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2021 Sep;14(9):1113-1131. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2021.1933436. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34015235 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological agents for the prevention of colistin-induced nephrotoxicity.Eur J Med Res. 2022 May 7;27(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s40001-022-00689-w. Eur J Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35525994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the Effectiveness of N-Acetylcysteine in the Prevention of Colistin-Induced Nephrotoxicity: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial.J Res Pharm Pract. 2022 May 25;10(4):159-165. doi: 10.4103/jrpp.jrpp_90_21. eCollection 2021 Oct-Dec. J Res Pharm Pract. 2022. PMID: 35769842 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin Attenuates Manganese-Induced Neuroinflammation by Alleviating Oxidative Stress through Regulation of Apoptosis, iNOS/NF-κB and HO-1/Nrf2 Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Sep 15;18(9):1989. doi: 10.3390/ijms18091989. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28914791 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin Attenuates Quinocetone-Induced Cell Apoptosis In Vitro by Activating the P38/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway and Inhibiting the ROS/Mitochondrial Apoptotic Pathway.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jul 30;11(8):1498. doi: 10.3390/antiox11081498. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36009217 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Effect of N-acetylcysteine in the Prevention of Colistin Nephrotoxicity in Critically Ill Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Res Pharm Pract. 2025 Mar 11;13(3):85-91. doi: 10.4103/jrpp.jrpp_55_24. eCollection 2024 Jul-Sep. J Res Pharm Pract. 2025. PMID: 40275970 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boucher HW, Talbot GH, Benjamin DK Jr, Bradley J, Guidos RJ, Jones RN, Murray BE, Bonomo RA, Gilbert D. 2013. 10 × ′20 Progress–development of new drugs active against gram-negative bacilli: an update from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis 56:1685–1694. doi:10.1093/cid/cit152. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akajagbor DS, Wilson SL, Shere-Wolfe KD, Dakum P, Charurat ME, Gilliam BL. 2013. Higher incidence of acute kidney injury with intravenous colistimethate sodium compared with polymyxin B in critically ill patients at a tertiary care medical center. Clin Infect Dis 57:1300–1303. doi:10.1093/cid/cit453. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

