Structure of Crumbs tail in complex with the PALS1 PDZ-SH3-GK tandem reveals a highly specific assembly mechanism for the apical Crumbs complex
- PMID: 25385611
- PMCID: PMC4267380
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1416515111
Structure of Crumbs tail in complex with the PALS1 PDZ-SH3-GK tandem reveals a highly specific assembly mechanism for the apical Crumbs complex
Abstract
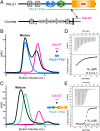
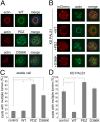
The Crumbs (Crb) complex, formed by Crb, PALS1, and PATJ, is evolutionarily conserved in metazoans and acts as a master cell-growth and -polarity regulator at the apical membranes in polarized epithelia. Crb intracellular functions, including its direct binding to PALS1, are mediated by Crb's highly conserved 37-residue cytoplasmic tail. However, the mechanistic basis governing the highly specific Crb-PALS1 complex formation is unclear, as reported interaction between the Crb tail (Crb-CT) and PALS1 PSD-95/DLG/ZO-1 (PDZ) domain is weak and promiscuous. Here we have discovered that the PDZ-Src homolgy 3 (SH3)-Guanylate kinase (GK) tandem of PALS1 binds to Crb-CT with a dissociation constant of 70 nM, which is ∼ 100-fold stronger than the PALS1 PDZ-Crb-CT interaction. The crystal structure of the PALS1 PDZ-SH3-GK-Crb-CT complex reveals that PDZ-SH3-GK forms a structural supramodule with all three domains contributing to the tight binding to Crb. Mutations disrupting the tertiary interactions of the PDZ-SH3-GK supramodule weaken the PALS1-Crb interaction and compromise PALS1-mediated polarity establishment in Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cysts. We further show that specific target binding of other members of membrane-associated guanylate kinases (MAGUKs) (e.g., CASK binding to neurexin) also requires the presence of their PDZ-SH3-GK tandems.
Keywords: MAGUK; PBM; Stardust; cell polarity; supramodule.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
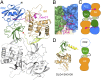



Comment in
-
MAGUKs end a tale of promiscuity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Dec 9;111(49):17350-1. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1420387111. Epub 2014 Nov 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25427803 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Structures of the human Pals1 PDZ domain with and without ligand suggest gated access of Crb to the PDZ peptide-binding groove.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2015 Mar;71(Pt 3):555-64. doi: 10.1107/S139900471402776X. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2015. PMID: 25760605 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for the phosphorylation-regulated interaction between the cytoplasmic tail of cell polarity protein crumbs and the actin-binding protein moesin.J Biol Chem. 2015 May 1;290(18):11384-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.643791. Epub 2015 Mar 19. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25792740 Free PMC article.
-
The Maguk protein, Pals1, functions as an adapter, linking mammalian homologues of Crumbs and Discs Lost.J Cell Biol. 2002 Apr 1;157(1):161-72. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200109010. Epub 2002 Apr 1. J Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11927608 Free PMC article.
-
The interdependence of the Rho GTPases and apicobasal cell polarity.Small GTPases. 2014;5(2):10. doi: 10.4161/21541248.2014.973768. Small GTPases. 2014. PMID: 25469537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of MAGUK-mediated cellular junctional complex organization.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2018 Feb;48:6-15. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2017.08.006. Epub 2017 Sep 14. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2018. PMID: 28917202 Review.
Cited by
-
MAGUKs end a tale of promiscuity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Dec 9;111(49):17350-1. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1420387111. Epub 2014 Nov 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25427803 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Cell polarity proteins and spermatogenesis.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016 Nov;59:62-70. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.06.008. Epub 2016 Jun 9. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27292315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanistic basis of MAGUK-organized complexes in synaptic development and signalling.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2016 Apr;17(4):209-23. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2016.18. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26988743 Review.
-
Correction to Binding of Crumbs to the Par-6 CRIB-PDZ Module Is Regulated by Cdc42.Biochemistry. 2016 Apr 5;55(13):2063. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00254. Epub 2016 Mar 25. Biochemistry. 2016. PMID: 27012924 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Crumbs is an essential regulator of cytoskeletal dynamics and cell-cell adhesion during dorsal closure in Drosophila.Elife. 2015 Nov 6;4:e07398. doi: 10.7554/eLife.07398. Elife. 2015. PMID: 26544546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tepass U. The apical polarity protein network in Drosophila epithelial cells: Regulation of polarity, junctions, morphogenesis, cell growth, and survival. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2012;28:655–685. - PubMed
-
- Martin-Belmonte F, Perez-Moreno M. Epithelial cell polarity, stem cells and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12(1):23–38. - PubMed
-
- Margolis B, Borg JP. Apicobasal polarity complexes. J Cell Sci. 2005;118(Pt 22):5157–5159. - PubMed
-
- Knust E, Bossinger O. Composition and formation of intercellular junctions in epithelial cells. Science. 2002;298(5600):1955–1959. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

