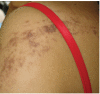
Unilateral Blaschkoid lichen planus in successive pregnancies
- PMID: 25386287
- PMCID: PMC4211518
- DOI: 10.4081/dr.2011.e35
Unilateral Blaschkoid lichen planus in successive pregnancies
Abstract
A number of genetic, congenital and acquired dermatoses have been known to follow Blaschko's lines. A common disorder like lichen planus can very rarely present with pruritic lesions in atypical patterns such as unilateral distribution, painful eruptions and along Blaschko's lines. Various triggering factors varying from viral infections and vaccinations to trauma have been implicated in lichen planus. We describe a female patient in the second trimester of her second pregnancy who developed unilateral lichen planus along Blaschko's lines during both pregnancies. No case of lichen planus along Blaschko's lines recurring during pregnancy is reported so far. Could pregnancy itself be a contributory factor towards onset of lichen planus in this case?
Keywords: Blaschko'slines.; lichen planus; pregnancy.
Figures
References
-
- Lehman JS, Tollefson MM, Gibson LE. Lichen planus. Int J Dermatol. 2009;48:682–94. - PubMed
-
- Bellman B, Reddy RK, Falanga V. Lichen planus associated with hepatitis C. Lancet. 1995;346:1234–1234. - PubMed
-
- Cribier B, Garnier C, Laustriat D, Heid E. Lichen planus and Hepatitis C virus infection: an epidemiologic study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;31:1070–2. - PubMed
-
- Harper JI, Trembath RC. Genetics and genodermatosis. In: Burns T, Breathnach S, Cox N, Griffith C, editors. Rook's Text book of Dermatology. 7th ed. Oxford: Blackwell Science; 2004. pp. 12–17.
-
- McGrath JA, Mclean WHI. Genetics in relation to skin. In: Wolff K, Goldsmith LA, Stephen IK, et al., editors. Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in general medicine. 7th ed. New York, NY: McGraw -Hill; 2008. pp. 83–83.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources