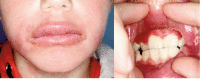
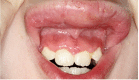
Orofacial Granulomatosis in Children can be the Initial Manifestation of Systemic Disease: A Presentation of Two Cases
- PMID: 25386323
- PMCID: PMC4223999
- DOI: 10.4081/dr.2014.5039
Orofacial Granulomatosis in Children can be the Initial Manifestation of Systemic Disease: A Presentation of Two Cases
Abstract
Orofacial granulomatosis is a chronic granulomatous condition characterized by relapsing and remitting lip swelling and oral involvement that may include deep ulcers, tags and cobblestone formation. It occurs as an independent entity but also in conjunction with systemic diseases such as tuberculosis, sarcoidosis and Crohn's disease. The clinical presentation is not indicative of concomitant systemic disease. To highlight the importance of thorough examination to rule out systemic disease, we present two childhood cases of orofacial granulomatosis, one of which was associated to Crohn's disease.
Keywords: Chron's disease; children; orofacial granulomatosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests: the authors declare no potential conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Sanderson J, Nunes C, Escudier M, et al. Oro-facial granulomatosis: Crohn’s disease or a new inflammatory bowel disease? Inflamm Bowel Dis 2005;11:840-6. - PubMed
-
- Campbell H, Escudier M, Patel P, et al. Distinguishing orofacial granulomatosis from Crohn’s disease: two separate disease entities? Inflamm Bowel Dis 2011;17:2109-15. - PubMed
-
- Tuxen AJ, Orchard D. Childhood and adolescent orofacial granulomatosis is strongly associated with Crohn’s disease and responds to intralesional corticosteroids. Australas J Dermatol 2010;51:124-7. - PubMed
-
- Tilakaratne WM, Freysdottir J, Fortune F. Orofacial granulomatosis: review on aetiology and pathogenesis. J Oral Pathol Med 2008;37:191-5. - PubMed
-
- Kemmler N, Pfannschmidt N, Strohal R. Orofacial granulomatosis as first manifestation of Crohn’s disease: successful treatment of both conditions with a combination of infliximab and dapsone. Acta Derm Venereol 2012;92:406-7. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources