Targeting the NFκB signaling pathways for breast cancer prevention and therapy
- PMID: 25386819
- PMCID: PMC6690202
- DOI: 10.2174/0929867321666141106124315
Targeting the NFκB signaling pathways for breast cancer prevention and therapy
Abstract
The activation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NFκB), a proinflammatory transcription factor, is a commonly observed phenomenon in breast cancer. It facilitates the development of a hormone-independent, invasive, high-grade, and late-stage tumor phenotype. Moreover, the commonly used cancer chemotherapy and radiotherapy approaches activate NFκB, leading to the development of invasive breast cancers that show resistance to chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and endocrine therapy. Inhibition of NFκB results in an increase in the sensitivity of cancer cells to the apoptotic effects of chemotherapeutic agents and radiation and restoring hormone sensitivity, which is correlated with increased disease-free survival in patients with breast cancer. In this review article, we focus on the role of the NFκB signaling pathways in the development and progression of breast cancer and the validity of NFκB as a potential target for breast cancer prevention and therapy. We also discuss the recent findings that NFκB may have tumor suppressing activity in certain cancer types. Finally, this review also covers the state-of-the-art development of NFκB inhibitors for cancer therapy and prevention, the challenges in targeting validation, and pharmacology and toxicology evaluations of these agents from the bench to the bedside.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors confirm that this article content has no conflict of interest.
Figures
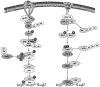
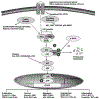
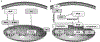
References
-
- Shacter E; Weitzman SA Chronic inflammation and cancer. Oncology (Williston Park), 2002, 16(2), 217–226, 229; discussion 230–232. - PubMed
-
- Lu H; Ouyang W; Huang C Inflammation, a key event in cancer development. Mol. Cancer Res, 2006, 4(4), 221–233. - PubMed
-
- Balkwill F; Mantovani A Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet, 2001, 357 (9255), 539–545. - PubMed
-
- Danese S Inflammatory bowel disease and inflammation-associated colon cancer: partners in crime. Curr. Drug Targets, 2008, 9(5), 360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

