Geriatric hospitalizations in fall-related injuries
- PMID: 25388273
- PMCID: PMC4232632
- DOI: 10.1186/s13049-014-0063-1
Geriatric hospitalizations in fall-related injuries
Abstract
Background: To investigate the injury pattern, severity, and mortality of elderly patients hospitalized for treatment of trauma following fall accidents.
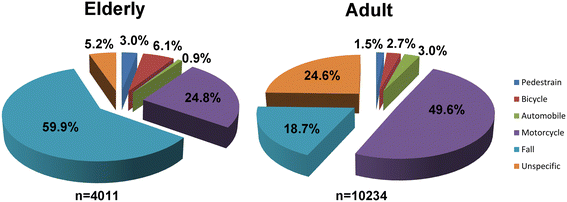
Methods: Data obtained from the Trauma Registry System were retrospectively reviewed for trauma admissions between January 1, 2009 and December 31, 2013 in a Level I trauma center. Of 16,548 registered patients, detailed information was retrieved from the 2,403 elderly patients (aged 65 years and above) with fall accidents and was compared with information from 1,909 adult patients (aged 20-64) with fall accidents.
Results: Falls presented the major mechanism for admission (59.9%) in the elderly patients. The number of elderly patients who fell from a height <1 m was greater than that of the adult patients (91.9% vs. 62.5%, respectively, p <0.001). The Injury Severity Score (ISS) (9.3 ± 4.4 vs. 8.3 ± 6.1, respectively, p =0.007) and New Injury Severity Score (NISS) (10.3 ± 6.8 vs. 9.5 ± 8.2, respectively, p <0.001) were significantly higher in the elderly than the adult patients. A significantly larger proportion of the elderly patients were admitted to the ICU (16.2% vs. 13.4%, respectively, p =0.009), and the elderly were found to have longer stays in the intensive care unit (ICU) (8.6 days vs. 7.6 days, respectively, p =0.034) but not in the hospital in general (9.6 days vs. 8.5 days, respectively, p =0.183). Additionally, a significantly higher percentage of the elderly patients sustained subdural hematoma (10.1% vs. 8.2%, respectively, p =0.032) and femoral fracture (50.6% vs. 14.1%, respectively, p <0.001). There were significant differences in in-hospital mortality (18.2% vs. 10.3%, respectively, p =0.031) and length of stay in the hospital (11.6 days vs. 14.9 days, respectively, p =0.037) between the elderly and adult patients with subdural hematoma, but not between those with femoral fracture.
Conclusions: Analysis of the data indicates that elderly patients hospitalized for treatment of trauma following fall accidents present with a bodily injury pattern that differs from that of adult patients and have a higher severe injury score, worse outcome, and higher mortality than those of adult patients.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical