Loss of estrogen-regulated microRNA expression increases HER2 signaling and is prognostic of poor outcome in luminal breast cancer
- PMID: 25388283
- PMCID: PMC4297564
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-1041
Loss of estrogen-regulated microRNA expression increases HER2 signaling and is prognostic of poor outcome in luminal breast cancer
Abstract
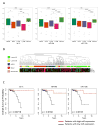
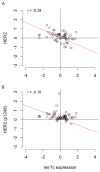
Among the genes regulated by estrogen receptor (ER) are miRNAs that play a role in breast cancer signaling pathways. To determine whether miRNAs are involved in ER-positive breast cancer progression to hormone independence, we profiled the expression of 800 miRNAs in the estrogen-dependent human breast cancer cell line MCF7 and its estrogen-independent derivative MCF7:2A (MCF7:2A) using NanoString. We found 78 miRNAs differentially expressed between the two cell lines, including a cluster comprising let-7c, miR99a, and miR125b, which is encoded in an intron of the long noncoding RNA LINC00478. These miRNAs are ER targets in MCF7 cells, and nearby ER binding and their expression are significantly decreased in MCF7:2A cells. The expression of these miRNAs was interrogated in patient samples profiled in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). Among luminal tumors, these miRNAs are expressed at higher levels in luminal A versus B tumors. Although their expression is uniformly low in luminal B tumors, they are lost only in a subset of luminal A patients. Interestingly, this subset with low expression of these miRNAs had worse overall survival compared with luminal A patients with high expression. We confirmed that miR125b directly targets HER2 and that let-7c also regulates HER2 protein expression. In addition, HER2 protein expression and activity are negatively correlated with let-7c expression in TCGA. In summary, we identified an ER-regulated miRNA cluster that regulates HER2, is lost with progression to estrogen independence, and may serve as a biomarker of poor outcome in ER(+) luminal A breast cancer patients.
©2014 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Charpentier AH, Bednarek AK, Daniel RL, Hawkins KA, Laflin KJ, Gaddis S, et al. Effects of estrogen on global gene expression: identification of novel targets of estrogen action. Cancer research. 2000;60:5977–83. - PubMed
-
- Frasor J, Danes JM, Komm B, Chang KC, Lyttle CR, Katzenellenbogen BS. Profiling of estrogen up- and down-regulated gene expression in human breast cancer cells: insights into gene networks and pathways underlying estrogenic control of proliferation and cell phenotype. Endocrinology. 2003;144:4562–74. - PubMed
-
- Carroll JS, Meyer CA, Song J, Li W, Geistlinger TR, Eeckhoute J, et al. Genome-wide analysis of estrogen receptor binding sites. Nature genetics. 2006;38:1289–97. - PubMed
-
- Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000;406:747–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

