Urinary elafin and kidney injury in hematopoietic cell transplant recipients
- PMID: 25388519
- PMCID: PMC4284403
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.01840214
Urinary elafin and kidney injury in hematopoietic cell transplant recipients
Abstract
Background and objectives: Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) is associated with kidney injury after hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT). Because plasma elafin levels correlate with skin GVHD, this study examined urinary elafin as a potential marker of renal inflammation and injury.
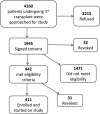
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Urine was collected prospectively on 205 patients undergoing their first HCT from 2003 to 2010. Collections were done at baseline, weekly through day 100, and monthly through year 1 to measure elafin and urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR). Associations between urinary elafin levels and microalbuminuria, macroalbuminuria, AKI and CKD, and mortality were examined using Cox proportional hazards or linear regression models. Available kidney biopsy specimens were processed for immunohistochemistry.
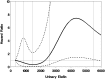
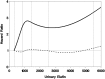
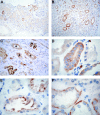
Results: Mean urinary elafin levels to day 100 were higher in patients with micro- or macroalbuminuria (adjusted mean difference, 529 pg/ml; P=0.03) at day 100 than in those with a normal ACR (adjusted mean difference, 1295 pg/ml; P<0.001). Mean urinary elafin levels were higher in patients with AKI compared with patients without AKI (adjusted mean difference, 558 pg/ml; P<0.01). The average urinary elafin levels within the first 100 days after HCT were higher in patients who developed CKD at 1 year than in patients without CKD (adjusted mean difference, 894 pg/ml; P=0.002). Among allogeneic recipients, a higher proportion of patients with micro- or macroalbuminuria at day 100 also had grade II-IV acute GVHD (80% and 86%, respectively) compared with patients with a normal ACR (58%; global P<0.01). Each increase in elafin of 500 pg/ml resulted in a 10% increase in risk of persistent macroalbuminuria (hazard ratio, 1.10; 95% confidence interval [95% CI], 1.06 to 1.13; P<0.001) and a 7% increase in the risk of overall mortality (95% CI, 1.02 to 1.13, P<0.01). Renal biopsy specimens from a separate cohort of HCT survivors demonstrated elafin staining in distal and collecting duct tubules.
Conclusion: Higher urinary elafin levels are associated with an increased risk of micro- and macroalbuminuria, AKI and CKD, and death after HCT.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; hematopoietic cell transplant; microalbuminuria; proteinuria; renal tubular epithelial cells.
Copyright © 2015 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chronic kidney disease in long-term survivors of hematopoietic cell transplant.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2007 Feb;39(4):223-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.bmt.1705573. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2007. PMID: 17290279
-
Changes in Glomerular Filtration Rate and Impact on Long-Term Survival among Adults after Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: A Prospective Cohort Study.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018 Jun 7;13(6):866-873. doi: 10.2215/CJN.10630917. Epub 2018 Apr 18. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29669818 Free PMC article.
-
GVHD-associated chronic kidney disease after allogeneic haematopoietic cell transplantation.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013 Oct;48(10):1329-34. doi: 10.1038/bmt.2013.55. Epub 2013 Apr 15. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013. PMID: 23584436
-
The kidney effects of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2014 Jan;21(1):96-105. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2013.08.007. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2014. PMID: 24359992 Review.
-
Alloreactivity as therapeutic principle in the treatment of hematologic malignancies. Studies of clinical and immunologic aspects of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with nonmyeloablative conditioning.Dan Med Bull. 2007 May;54(2):112-39. Dan Med Bull. 2007. PMID: 17521527 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical significance of PI3 and HLA-DOB as potential prognostic predicators for ovarian cancer.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Feb;9(2):466-476. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2019.11.30. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117391 Free PMC article.
-
Allogeneic T cells cause acute renal injury after hematopoietic cell transplantation.Blood Adv. 2023 Nov 28;7(22):6936-6948. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2023009721. Blood Adv. 2023. PMID: 37748044 Free PMC article.
-
Mini-review of kidney disease following hematopoietic stem cell transplant .Clin Nephrol. 2018 Jun;89(6):389-402. doi: 10.5414/CN109276. Clin Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29578399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toward a Better Understanding of the Atypical Features of Chronic Graft-Versus-Host Disease: A Report from the 2020 National Institutes of Health Consensus Project Task Force.Transplant Cell Ther. 2022 Aug;28(8):426-445. doi: 10.1016/j.jtct.2022.05.038. Epub 2022 May 31. Transplant Cell Ther. 2022. PMID: 35662591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute kidney injury in HCT: an update.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016 Jun;51(6):755-62. doi: 10.1038/bmt.2015.357. Epub 2016 Feb 8. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016. PMID: 26855155 Review.
References
-
- Hingorani S, Guthrie KA, Schoch G, Weiss NS, McDonald GB: Chronic kidney disease in long-term survivors of hematopoietic cell transplant. Bone Marrow Transplant 39: 223–229, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Malone FR, Leisenring WM, Storer BE, Lawler R, Stern JM, Aker SN, Bouvier ME, Martin PJ, Batchelder AL, Schoch HG, McDonald GB: Prolonged anorexia and elevated plasma cytokine levels following myeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant. Bone Marrow Transplant 40: 765–772, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Luft T, Dietrich S, Falk C, Conzelmann M, Hess M, Benner A, Neumann F, Isermann B, Hegenbart U, Ho AD, Dreger P: Steroid-refractory GVHD: T-cell attack within a vulnerable endothelial system. Blood 118: 1685–1692, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Tichelli A, Gratwohl A: Vascular endothelium as ‘novel’ target of graft-versus-host disease. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 21: 139–148, 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

