Exploring the role of two interacting phosphoinositide 3-kinases of Haemonchus contortus
- PMID: 25388625
- PMCID: PMC4233088
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-014-0498-2
Exploring the role of two interacting phosphoinositide 3-kinases of Haemonchus contortus
Abstract
Background: Phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks) are relatively conserved and important intracellular lipid kinases involved in signalling and other biological pathways. In the free-living nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, the heterodimeric form of PI3K consists of catalytic (AGE-1) and regulatory (AAP-1) subunits. These subunits are key components of the insulin-like signalling pathway and play roles in the regulation of the entry into and exit from dauer. Although, in parasitic nematodes, similar components are proposed to regulate the transition from free-living or arrested stages to parasitic larvae, nothing is known about PI3Ks in relation to the transition of third-stage larvae (L3s) to parasitism in Haemonchus contortus.
Methods: An integrated molecular approach was used to investigate age-1 and aap-1 of H. contortus (Hc-age-1 and Hc-aap-1) in C. elegans.
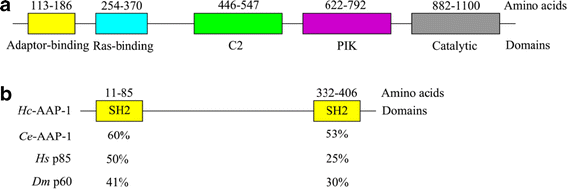
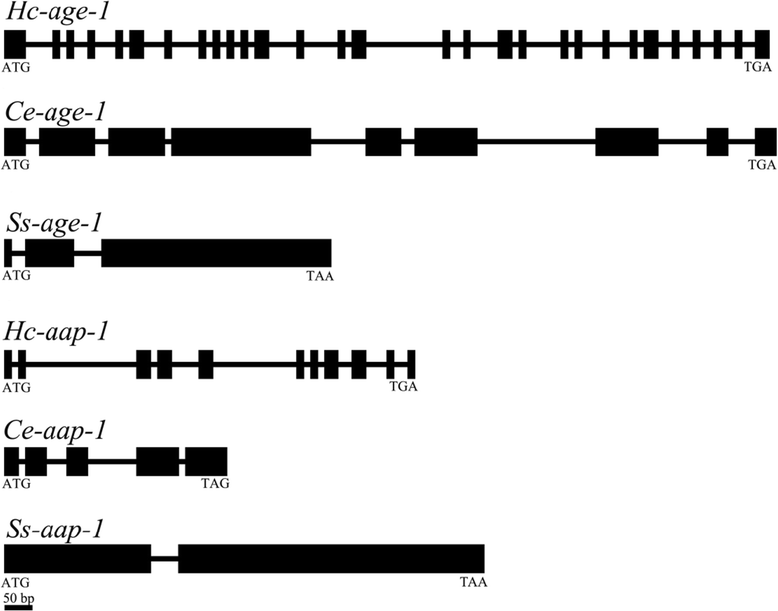
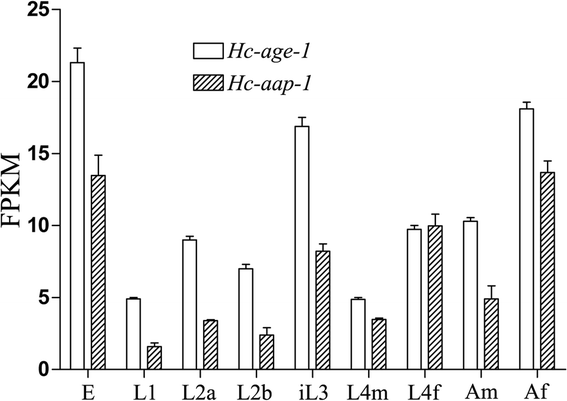
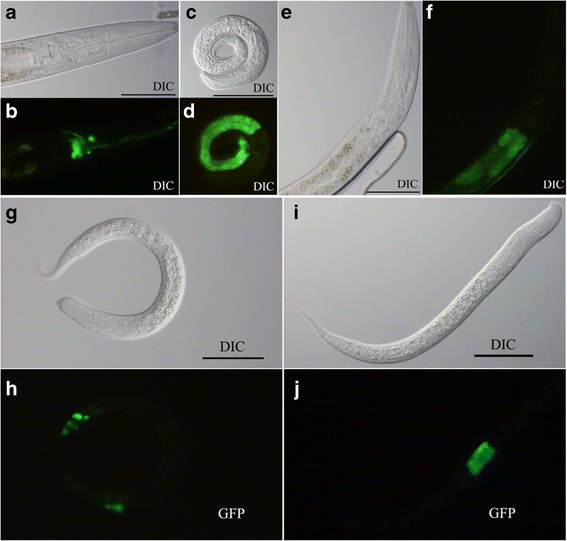
Results: The two genes Hc-age-1 and Hc-aap-1 were transcribed in all life stages, with the highest levels in the egg, infective L3 and adult female of H. contortus. The expression of these genes was localized to the intestine, contrasting the pattern of their orthologues in C. elegans (where they are expressed in both head neurons and the intestine). The yeast two-hybrid analysis demonstrated that the adaptor-binding domain of Hc-AGE-1 interacted strongly with the Hc-AAP-1; however, this complex did not rescue the function of its orthologue in age-1-deficient C. elegans.
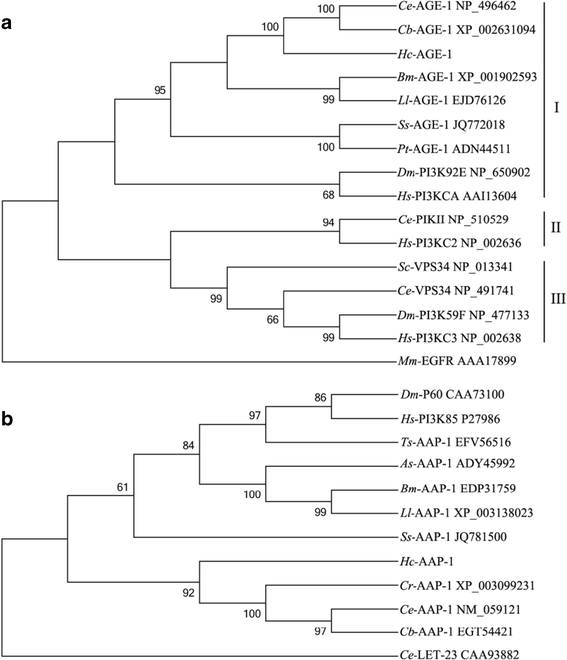
Conclusions: This is the first time that the PI3K-encoding genes have been characterized from a strongylid parasitic nematode. The findings provide insights into the role of the PI3K heterodimer represented by Hc-age-1 and Hc-aap-1 in the developmental biology of H. contortus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular characterization of the Haemonchus contortus phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 gene (Hc-pdk-1).Parasit Vectors. 2016 Feb 3;9:65. doi: 10.1186/s13071-016-1351-6. Parasit Vectors. 2016. PMID: 26842781 Free PMC article.
-
Hc-daf-2 encodes an insulin-like receptor kinase in the barber's pole worm, Haemonchus contortus, and restores partial dauer regulation.Int J Parasitol. 2014 Jun;44(7):485-96. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2014.03.005. Epub 2014 Apr 12. Int J Parasitol. 2014. PMID: 24727120 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional characterisation of the fork head transcription factor-encoding gene, Hc-daf-16, from the parasitic nematode Haemonchus contortus (Strongylida).Int J Parasitol. 2010 Mar 15;40(4):405-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2009.09.005. Epub 2009 Sep 29. Int J Parasitol. 2010. PMID: 19796644 Free PMC article.
-
Prospects for exploring molecular developmental processes in Haemonchus contortus.Int J Parasitol. 2006 Jul;36(8):859-68. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2006.04.007. Epub 2006 May 17. Int J Parasitol. 2006. PMID: 16759659 Review.
-
Elucidating the molecular and developmental biology of parasitic nematodes: Moving to a multiomics paradigm.Adv Parasitol. 2020;108:175-229. doi: 10.1016/bs.apar.2019.12.005. Epub 2020 Jan 31. Adv Parasitol. 2020. PMID: 32291085 Review.
Cited by
-
The Haemonchus contortus kinome--a resource for fundamental molecular investigations and drug discovery.Parasit Vectors. 2015 Dec 8;8:623. doi: 10.1186/s13071-015-1231-5. Parasit Vectors. 2015. PMID: 26644012 Free PMC article.
-
On the role of dauer in the adaptation of nematodes to a parasitic lifestyle.Parasit Vectors. 2021 Oct 27;14(1):554. doi: 10.1186/s13071-021-04953-6. Parasit Vectors. 2021. PMID: 34706780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reconstruction of the insulin-like signalling pathway of Haemonchus contortus.Parasit Vectors. 2016 Feb 3;9:64. doi: 10.1186/s13071-016-1341-8. Parasit Vectors. 2016. PMID: 26842675 Free PMC article.
-
A TGF-β type II receptor that associates with developmental transition in Haemonchus contortus in vitro.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019 Dec 2;13(12):e0007913. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007913. eCollection 2019 Dec. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019. PMID: 31790412 Free PMC article.
-
PI3K/AKT signaling in parasites and parasite diseases: Role and therapeutic potential.Virulence. 2025 Dec;16(1):2532803. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2025.2532803. Epub 2025 Jul 15. Virulence. 2025. PMID: 40643963 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

