How can we better identify early HIV infections?
- PMID: 25389806
- PMCID: PMC4490585
- DOI: 10.1097/COH.0000000000000121
How can we better identify early HIV infections?
Abstract
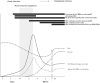
Purpose of review: Detection of early HIV infections (EHIs), including acute HIV infection (AHI), is important for individual health, prevention of HIV transmission, and measurement of HIV incidence. We describe markers of EHI, diagnostic strategies for detecting these markers, and ways to incorporate these strategies into diagnostic and HIV incidence algorithms.
Recent findings: For individual diagnosis in the USA and Europe, laboratory-based diagnostic algorithms increasingly incorporate fourth-generation HIV antigen tests, allowing for earlier detection. In some sub-Saharan African settings, symptom-based screening is being explored to identify subsets of persons at high risk for AHI. Point-of-care diagnostics designed for AHI detection are in the pipeline and, if validated, represent an opportunity for real-time AHI diagnosis. At the population level, multiassay algorithms are promising new strategies for estimating HIV incidence on the basis of several assays applied to cross-sectional samples. These algorithms can be developed to optimize performance, in addition to cost and logistical considerations.
Summary: There are important recent advances in detection of EHIs at the individual and population levels. Applying optimal combinations of tests in diagnostic and HIV incidence algorithms is urgently needed to support the multiple goals derived from enhanced detection and discrimination of EHIs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Fiebig EW, Wright DJ, Rawal BD, et al. Dynamics of HIV viremia and antibody seroconversion in plasma donors: implications for diagnosis and staging of primary HIV infection. AIDS. 2003;17:1871–1879. - PubMed
-
- Lavreys L, Baeten JM, Chohan V, et al. Higher set point plasma viral load and more-severe acute HIV type 1 (HIV-1) illness predict mortality among high-risk HIV-1-infected African women. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;42:1333–1339. - PubMed
-
- Ananworanich J, Fletcher JL, Pinyakorn S, et al. A novel acute HIV infection staging system based on 4th generation immunoassay. Retrovirology. 2013;10:56. Fourth-generation immunoassays can be used as part of an AHI staging system, distinguishing different groups of recently infected persons. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sanders EJ, Mugo P, Prins HA, et al. Acute HIV-1 infection is as common as malaria in young febrile adults seeking care in coastal Kenya. AIDS. 2014;28:1357–63. AHI was as common as malaria in young febrile adults, suggesting an AHI detection strategy targeting febrile young adults is feasible and important. - PMC - PubMed

