Related neuropeptides use different balances of unitary mechanisms to modulate the cardiac neuromuscular system in the American lobster, Homarus americanus
- PMID: 25392168
- PMCID: PMC4312872
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00585.2014
Related neuropeptides use different balances of unitary mechanisms to modulate the cardiac neuromuscular system in the American lobster, Homarus americanus
Abstract
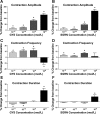
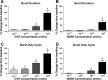
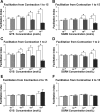
To produce flexible outputs, neural networks controlling rhythmic motor behaviors can be modulated at multiple levels, including the pattern generator itself, sensory feedback, and the response of the muscle to a given pattern of motor output. We examined the role of two related neuropeptides, GYSDRNYLRFamide (GYS) and SGRNFLRFamide (SGRN), in modulating the neurogenic lobster heartbeat, which is controlled by the cardiac ganglion (CG). When perfused though an isolated whole heart at low concentrations, both peptides elicited increases in contraction amplitude and frequency. At higher concentrations, both peptides continued to elicit increases in contraction amplitude, but GYS caused a decrease in contraction frequency, while SGRN did not alter frequency. To determine the sites at which these peptides induce their effects, we examined the effects of the peptides on the periphery and on the isolated CG. When we removed the CG and stimulated the motor nerve with constant bursts of stimuli, both GYS and SGRN increased contraction amplitude, indicating that each peptide modulates the muscle or the neuromuscular junction. When applied to the isolated CG, neither peptide altered burst frequency at low peptide concentrations; at higher concentrations, SGRN decreased burst frequency, whereas GYS continued to have no effect on frequency. Together, these data suggest that the two peptides elicit some of their effects using different mechanisms; in particular, given the known feedback pathways within this system, the importance of the negative (nitric oxide) relative to the positive (stretch) feedback pathways may differ in the presence of the two peptides.
Keywords: FMRFamide-like peptide; cardiac ganglion; feedback.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures






References
-
- Alexandrowicz JS. The innervation of the heart of the Crustacea. I Decapoda. Q J Microsc Sci 75: 181–249, 1932.
-
- Anderson M, Cooke IM. Neural activation of the heart of the lobster Homarus americanus. J Exp Biol 55: 449–468, 1971. - PubMed
-
- Beilin SA, Pasztor VM. Modulation of a rhythmically active crayfish muscle by the neuropeptide proctolin. Can J Zool 67: 73–81, 1989.
-
- Bendena WG, Garside CS, Yu CG, Tobe SS. Allatostatins: diversity in structure and function of an insect neuropeptide family. Ann NY Acad Sci 814: 53–66, 1997. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

