Whole-genome sequencing confirms that Burkholderia pseudomallei multilocus sequence types common to both Cambodia and Australia are due to homoplasy
- PMID: 25392354
- PMCID: PMC4290968
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02574-14
Whole-genome sequencing confirms that Burkholderia pseudomallei multilocus sequence types common to both Cambodia and Australia are due to homoplasy
Abstract
Burkholderia pseudomallei isolates with shared multilocus sequence types (STs) have not been isolated from different continents. We identified two STs shared between Australia and Cambodia. Whole-genome analysis revealed substantial diversity within STs, correctly identified the Asian or Australian origin, and confirmed that these shared STs were due to homoplasy.
Copyright © 2015, De Smet et al.
Figures
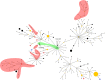
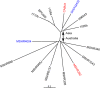
References
-
- Dale J, Price EP, Hornstra H, Busch JD, Mayo M, Godoy D, Wuthiekanun V, Baker A, Foster JT, Wagner DM, Tuanyok A, Warner J, Spratt BG, Peacock SJ, Currie BJ, Keim P, Pearson T. 2011. Epidemiological tracking and population assignment of the non-clonal bacterium, Burkholderia pseudomallei. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 5:e1381. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0001381. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pearson T, Giffard P, Beckstrom-Sternberg S, Auerbach R, Hornstra H, Tuanyok A, Price EP, Glass MB, Leadem B, Beckstrom-Sternberg JS, Allan GJ, Foster JT, Wagner DM, Okinaka RT, Sim SH, Pearson O, Wu Z, Chang J, Kaul R, Hoffmaster AR, Brettin TS, Robison RA, Mayo M, Gee JE, Tan P, Currie BJ, Keim P. 2008. Phylogeographic reconstruction of a bacterial species with high levels of lateral gene transfer. BMC Biol 18:7. doi:10.1186/1741-7007-7-78. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

