Gut microbes and the brain: paradigm shift in neuroscience
- PMID: 25392516
- PMCID: PMC4228144
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3299-14.2014
Gut microbes and the brain: paradigm shift in neuroscience
Abstract
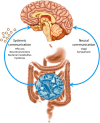
The discovery of the size and complexity of the human microbiome has resulted in an ongoing reevaluation of many concepts of health and disease, including diseases affecting the CNS. A growing body of preclinical literature has demonstrated bidirectional signaling between the brain and the gut microbiome, involving multiple neurocrine and endocrine signaling mechanisms. While psychological and physical stressors can affect the composition and metabolic activity of the gut microbiota, experimental changes to the gut microbiome can affect emotional behavior and related brain systems. These findings have resulted in speculation that alterations in the gut microbiome may play a pathophysiological role in human brain diseases, including autism spectrum disorder, anxiety, depression, and chronic pain. Ongoing large-scale population-based studies of the gut microbiome and brain imaging studies looking at the effect of gut microbiome modulation on brain responses to emotion-related stimuli are seeking to validate these speculations. This article is a summary of emerging topics covered in a symposium and is not meant to be a comprehensive review of the subject.
Copyright © 2014 the authors 0270-6474/14/3415490-07$15.00/0.
Figures
References
-
- Ahluwalia V, Wade JB, Heuman DM, Hammeke TA, Sanyal AJ, Sterling RK, Stravitz RT, Luketic V, Siddiqui MS, Puri P, Fuchs M, Lennon MJ, Kraft KA, Gilles H, White MB, Noble NA, Bajaj JS. Enhancement of functional connectivity, working memory and inhibitory control on multi-modal brain MR imaging with rifaximin in cirrhosis: implications for the gut-liver-brain axis. Metab Brain Dis. 2014 doi: 10.1007/s11011-014-9507-6. doi: 10.1007/s11011-014-9507-6. Advance online publication. Retrieved Mar. 4, 2014. - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bajaj JS, Heuman DM, Sanyal AJ, Hylemon PB, Sterling RK, Stravitz RT, Fuchs M, Ridlon JM, Daita K, Monteith P, Noble NA, White MB, Fisher A, Sikaroodi M, Rangwala H, Gillevet PM. Modulation of the metabiome by rifaximin in patients with cirrhosis and minimal hepatic encephalopathy. PLoS One. 2013;8:e60042. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060042. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
