Post-hepatectomy liver failure
- PMID: 25392835
- PMCID: PMC4207837
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2304-3881.2014.09.01
Post-hepatectomy liver failure
Abstract
Hepatectomies are among some of the most complex operative interventions performed. Mortality rates after major hepatectomy are as high as 30%, with post-hepatic liver failure (PHLF) representing the major source of morbidity and mortality. We present a review of PHLF, including the current definition, predictive factors, pre-operative risk assessment, techniques to prevent PHLF, identification and management. Despite great improvements in morbidity and mortality, liver surgery continues to demand excellent clinical judgement in selecting patients for surgery. Appropriate choice of pre-operative techniques to improve the functional liver remnant (FLR), fastidious surgical technique, and excellent post-operative management are essential to optimize patient outcomes.
Keywords: Post-hepatectomy liver failure (PHLF); predictive factors for liver failure; prevention of liver failure.
Figures
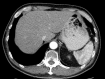
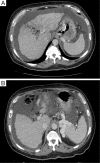
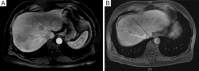
References
-
- Ong GB, Lee NW. Hepatic resection. Br J Surg 1975;62:421-30. - PubMed
-
- Rahbari NN, Garden OJ, Padbury R, et al. Posthepatectomy liver failure: a definition and grading by the International Study Group of Liver Surgery (ISGLS). Surgery 2011;149:713-24. - PubMed
-
- Paugam-Burtz C, Janny S, Delefosse D, et al. Prospective validation of the "fifty-fifty" criteria as an early and accurate predictor of death after liver resection in intensive care unit patients. Ann Surg 2009;249:124-8. - PubMed
-
- Jaeck D, Bachellier P, Oussoultzoglou E, et al. Surgical resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Post-operative outcome and long-term results in Europe: an overview. Liver Transpl 2004;10:S58-63. - PubMed
-
- Ren Z, Xu Y, Zhu S.Indocyanine green retention test avoiding liver failure after hepatectomy for hepatolithiasis. Hepatogastroenterology 2012;59:782-4. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
