Identification of a common non-apoptotic cell death mechanism in hereditary retinal degeneration
- PMID: 25392995
- PMCID: PMC4230983
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112142
Identification of a common non-apoptotic cell death mechanism in hereditary retinal degeneration
Abstract
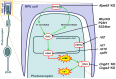
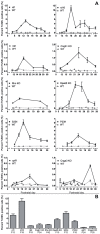
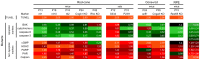
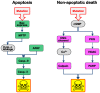
Cell death in neurodegenerative diseases is often thought to be governed by apoptosis; however, an increasing body of evidence suggests the involvement of alternative cell death mechanisms in neuronal degeneration. We studied retinal neurodegeneration using 10 different animal models, covering all major groups of hereditary human blindness (rd1, rd2, rd10, Cngb1 KO, Rho KO, S334ter, P23H, Cnga3 KO, cpfl1, Rpe65 KO), by investigating metabolic processes relevant for different forms of cell death. We show that apoptosis plays only a minor role in the inherited forms of retinal neurodegeneration studied, where instead, a non-apoptotic degenerative mechanism common to all mutants is of major importance. Hallmark features of this pathway are activation of histone deacetylase, poly-ADP-ribose-polymerase, and calpain, as well as accumulation of cyclic guanosine monophosphate and poly-ADP-ribose. Our work thus demonstrates the prevalence of alternative cell death mechanisms in inherited retinal degeneration and provides a rational basis for the design of mutation-independent treatments.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B, Nicotera P (2003) Regulation of cell death: the calcium-apoptosis link. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4: 552–565. - PubMed
-
- Chang GQ, Hao Y, Wong F (1993) Apoptosis: final common pathway of photoreceptor death in rd, rds, and rhodopsin mutant mice. Neuron 11: 595–605. - PubMed
-
- Marigo V (2007) Programmed cell death in retinal degeneration: targeting apoptosis in photoreceptors as potential therapy for retinal degeneration. Cell Cycle 6: 652–655. - PubMed
-
- Yoshizawa K, Kiuchi K, Nambu H, Yang J, Senzaki H, et al. (2002) Caspase-3 inhibitor transiently delays inherited retinal degeneration in C3H mice carrying the rd gene. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 240: 214–219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

