Frailty, mycophenolate reduction, and graft loss in kidney transplant recipients
- PMID: 25393156
- PMCID: PMC4382409
- DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000000444
Frailty, mycophenolate reduction, and graft loss in kidney transplant recipients
Abstract
Background: Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) side effects often prompt dose reduction or discontinuation, and this MMF dose reduction (MDR) can lead to rejection and possibly graft loss. Unfortunately, little is known about what factors might cause or contribute to MDR. Frailty, a measure of physiologic reserve, is emerging as an important, novel domain of risk in kidney transplantation recipients. We hypothesized that frailty, an inflammatory phenotype, might be associated with MDR.
Methods: We measured frailty (shrinking, weakness, exhaustion, low physical activity, and slowed walking speed), other patient and donor characteristics, longitudinal MMF doses, and graft loss in 525 kidney transplantation recipients. Time-to-MDR was quantified using an adjusted Cox proportional hazards model.
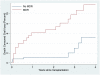
Results: By 2 years after transplantation, 54% of frail recipients and 45% of nonfrail recipients experienced MDR; by 4 years, incidence was 67% and 51%. Frail recipients were 1.29 times (95% confidence interval [95% CI], 1.01-1.66; P = 0.04) more likely to experience MDR, as were deceased donor recipients (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.92; 95% CI, 1.44-2.54, P < 0.001) and older adults (age ≥ 65 vs <65; aHR, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.10-1.96, P = 0.01). Mycophenolate mofetil dose reduction was independently associated with a substantially increased risk of death-censored graft loss (aHR, 5.24; 95% CI, 1.97-13.98, P = 0.001).
Conclusion: A better understanding of risk factors for MMF intolerance might help in planning alternate strategies to maintain adequate immunosuppression and prolong allograft survival.
Figures

References
-
- Maripuri S, Kasiske BL. The role of mycophenolate mofetil in kidney transplantation revisited. Transplant Rev (Orlando) 2014;28(1):26. - PubMed
-
- Pelletier RP, Akin B, Henry ML, et al. The impact of mycophenolate mofetil dosing patterns on clinical outcome after renal transplantation. Clin Transplant. 2003;17(3):200. - PubMed
-
- Knoll GA, MacDonald I, Khan A, Van Walraven C. Mycophenolate mofetil dose reduction and the risk of acute rejection after renal transplantation. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14(9):2381. - PubMed
-
- Kahu J, Kyllonen L, Salmela K. Impact of mycophenolate mofetil intolerance on early results of kidney transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2005;37(8):3276. - PubMed
-
- Ortega F, Sanchez-Fructuoso A, Cruzado JM, et al. Gastrointestinal quality of life improvement of renal transplant recipients converted from mycophenolate mofetil to enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium drugs or agents: mycophenolate mofetil and enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium. Transplantation. 2011;92(4):426. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F32 AG044994/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- F32DK093218/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AG000247/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AG021334/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- F32AG044994/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007024/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG021334/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AG043501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK093218/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG042504/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG042504/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK101828/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01AG043501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32AG000247/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

