Docosahexaenoic acid induces the degradation of HPV E6/E7 oncoproteins by activating the ubiquitin-proteasome system
- PMID: 25393480
- PMCID: PMC4260735
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2014.477
Docosahexaenoic acid induces the degradation of HPV E6/E7 oncoproteins by activating the ubiquitin-proteasome system
Abstract
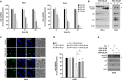
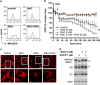
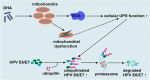
The oncogenic human papillomavirus (HPV) E6/E7 proteins are essential for the onset and maintenance of HPV-associated malignancies. Here, we report that activation of the cellular ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) by the omega-3 fatty acid, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), leads to proteasome-mediated degradation of E6/E7 viral proteins and the induction of apoptosis in HPV-infected cancer cells. The increases in UPS activity and degradation of E6/E7 oncoproteins were associated with DHA-induced overproduction of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS). Exogenous oxidative stress and pharmacological induction of mitochondrial ROS showed effects similar to those of DHA, and inhibition of ROS production abolished UPS activation, E6/E7 viral protein destabilization, and apoptosis. These findings identify a novel role for DHA in the regulation of UPS and viral proteins, and provide evidence for the use of DHA as a mechanistically unique anticancer agent for the chemoprevention and treatment of HPV-associated tumors.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Mapping the interactome of HPV E6 and E7 oncoproteins with the ubiquitin-proteasome system.FEBS J. 2017 Oct;284(19):3171-3201. doi: 10.1111/febs.14193. Epub 2017 Aug 29. FEBS J. 2017. PMID: 28786561
-
Marine Streptomyces sp. derived antimycin analogues suppress HeLa cells via depletion HPV E6/E7 mediated by ROS-dependent ubiquitin-proteasome system.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 8;7:42180. doi: 10.1038/srep42180. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28176847 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Wnt signaling pathway by human papillomavirus E6 and E7 oncogenes in HPV16-positive oropharyngeal squamous carcinoma cells.Mol Cancer Res. 2010 Mar;8(3):433-43. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0345. Epub 2010 Mar 9. Mol Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20215420
-
The HPV E6/E7 Oncogenes: Key Factors for Viral Carcinogenesis and Therapeutic Targets.Trends Microbiol. 2018 Feb;26(2):158-168. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2017.07.007. Epub 2017 Aug 17. Trends Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 28823569 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms underlying human papillomavirus E6 and E7 oncoprotein-induced cell transformation.Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2017 Apr-Jun;772:23-35. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2016.08.001. Epub 2016 Aug 5. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 2017. PMID: 28528687 Review.
Cited by
-
Toxicity and Functional Tissue Responses of Two Freshwater Fish after Exposure to Polystyrene Microplastics.Toxics. 2021 Nov 2;9(11):289. doi: 10.3390/toxics9110289. Toxics. 2021. PMID: 34822680 Free PMC article.
-
Perspectives of lipid metabolism reprogramming in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: An overview.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 16;12:1008361. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1008361. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36185215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Docosahexaenoic acid inhibits zymogen activation by suppressing vacuolar ATPase activation in cerulein-stimulated pancreatic acinar cells.Genes Nutr. 2020 Mar 23;15(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12263-020-00664-2. Genes Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32293245 Free PMC article.
-
Pronounced Enhancement in Radiosensitization of Esophagus Cancer Cultivated in Docosahexaenoic Acid via the PPAR -γ Activation.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 22;9:922228. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.922228. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 37153924 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of Fe/Cu -chelators and docosahexaenoic acid: an exploration for the treatment of colorectal cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 May 11;8(31):51478-51491. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17807. eCollection 2017 Aug 1. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28881661 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zandberg DP, Bhargava R, Badin S, Cullen KJ. The role of human papillomavirus in nongenital cancers. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:57–81. - PubMed
-
- Wentzensen N, Vinokurova S, von Knebel Doeberitz M. Systematic review of genomic integration sites of human papillomavirus genomes in epithelial dysplasia and invasive cancer of the female lower genital tract. Cancer Res. 2004;64:3878–3884. - PubMed
-
- Moody CA, Laimins LA. Human papillomavirus oncoproteins: pathways to transformation. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:550–560. - PubMed
-
- Yugawa T, Kiyono T. Molecular mechanisms of cervical carcinogenesis by high-risk human papillomaviruses: novel functions of E6 and E7 oncoproteins. Rev Med Virol. 2009;19:97–113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

