Performance evaluation of the Xpert MTB/RIF assay according to its clinical application
- PMID: 25395048
- PMCID: PMC4247199
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-014-0589-x
Performance evaluation of the Xpert MTB/RIF assay according to its clinical application
Abstract
Background: The Xpert MTB/RIF assay (Xpert assay; Cepheid, Sunnyvale, CA) is becoming the test of choice for the rapid diagnosis of tuberculosis and rifampin (RIF) resistance. The aim of this study was to evaluate the performance of the Xpert assay with respect to its clinical application at a tertiary care hospital in Korea, a country with an intermediate tuberculosis burden and high-resource.
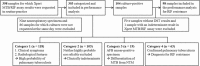
Methods: A total of 303 Xpert assay results from 109 smear-positive and 194 smear-negative respiratory specimens were retrospectively reviewed. Based on patients' medical records, four categories of clinical applications of the Xpert assay were identified: (1) the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis in patients with a high probability of pulmonary tuberculosis according to their clinical and radiological features; (2) the exclusion of tuberculosis in clinically indeterminate patients for pulmonary tuberculosis; (3) the differentiation of Mycobacterium tuberculsosis (MTB) from nontuberculous mycobacteria in a smear-positive specimen; and (4) the diagnosis of RIF resistance. Standard culture and drug susceptibility tests were used as reference methods.
Results: The sensitivity of the Xpert assay for MTB detection in category 1 was 89.8% (95% confidence interval [CI], 78.5-95.8%), but 66.7% (95% CI, 12.5-98.2%) in category 2. The positive predictive values ranged from 33.3% (95% CI, 6.0-75.9%) in category 2 to 91.3% and 91.7% in categories 1 and 3, respectively. The negative predictive values were over 90% in all categories. The Xpert assay correctly detected RIF resistance in six of the seven (85.7%) isolates tested.
Conclusions: The Xpert assay exhibited variable performance according to its clinical application; this finding cautions that careful interpretation for the results of this assay would be needed according to its intended purpose.
Figures
References
-
- Helb D, Jones M, Story E, Boehme C, Wallace E, Ho K, Kop J, Owens MR, Rodgers R, Banada P, Safi H, Blakemore R, Lan NT, Jones-López EC, Levi M, Burday M, Ayakaka I, Mugerwa RD, McMillan B, Winn-Deen E, Christel L, Dailey P, Perkins MD, Persing DH, Alland D. Rapid detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosisand rifampin resistance by use of on-demand, near-patient technology. J Clin Microbiol. 2010;48(1):229–237. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01463-09. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boehme CC, Nabeta P, Hillemann D, Nicol MP, Shenai S, Krapp F, Allen J, Tahirli R, Blakemore R, Rustomjee R, Milovic A, Jones M, O’Brien SM, Persing DH, Ruesch-Gerdes S, Gotuzzo E, Rodrigues C, Alland D, Perkins MD. Rapid molecular detection of tuberculosis and rifampin resistance. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(11):1005–1015. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0907847. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boehme CC, Nicol MP, Nabeta P, Michael JS, Gotuzzo E, Tahirli R, Gler MT, Blakemore R, Worodria W, Gray C, Huang L, Caceres T, Mehdiyev R, Raymond L, Whitelaw A, Sagadevan K, Alexander H, Albert H, Cobelens F, Cox H, Alland D, Perkins MD. Feasibility, diagnostic accuracy, and effectiveness of decentralised use of the Xpert MTB/RIF test for diagnosis of tuberculosis and multidrug resistance: a multicentre implementation study. Lancet. 2011;377(9776):1495–1505. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60438-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rachow A, Zumla A, Heinrich N, Rojas-Ponce G, Mtafya B, Reither K, Ntinginya EN, O'Grady J, Huggett J, Dheda K, Boehme C, Perkins M, Saathoff E, Hoelscher M. Rapid and accurate detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosisin sputum samples by Cepheid Xpert MTB/RIF assay-a clinical validation study. PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e20458. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020458. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical