Inflammatory signaling regulates embryonic hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell production
- PMID: 25395663
- PMCID: PMC4248291
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.253302.114
Inflammatory signaling regulates embryonic hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell production
Abstract
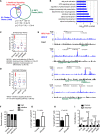
Identifying signaling pathways that regulate hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell (HSPC) formation in the embryo will guide efforts to produce and expand HSPCs ex vivo. Here we show that sterile tonic inflammatory signaling regulates embryonic HSPC formation. Expression profiling of progenitors with lymphoid potential and hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) from aorta/gonad/mesonephros (AGM) regions of midgestation mouse embryos revealed a robust innate immune/inflammatory signature. Mouse embryos lacking interferon γ (IFN-γ) or IFN-α signaling and zebrafish morphants lacking IFN-γ and IFN-ϕ activity had significantly fewer AGM HSPCs. Conversely, knockdown of IFN regulatory factor 2 (IRF2), a negative regulator of IFN signaling, increased expression of IFN target genes and HSPC production in zebrafish. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) combined with sequencing (ChIP-seq) and expression analyses demonstrated that IRF2-occupied genes identified in human fetal liver CD34(+) HSPCs are actively transcribed in human and mouse HSPCs. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the primitive myeloid population contributes to the local inflammatory response to impact the scale of HSPC production in the AGM region. Thus, sterile inflammatory signaling is an evolutionarily conserved pathway regulating the production of HSPCs during embryonic development.
Keywords: hematopoiesis; hematopoietic stem cell; interferon; lymphoid progenitor; mouse; zebrafish.
© 2014 Li et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures






References
-
- Abrahams VM. 2008. Pattern recognition at the maternal-fetal interface. Immunol Invest 37: 427–447. - PubMed
-
- Anderson KV, Bokla L, Nusslein-Volhard C. 1985. Establishment of dorsal-ventral polarity in the Drosophila embryo: the induction of polarity by the Toll gene product. Cell 42: 791–798. - PubMed
-
- Balounova J, Vavrochova T, Benesova M, Ballek O, Kolar M, Filipp D. 2014. Toll-like receptors expressed on embryonic macrophages couple inflammatory signals to iron metabolism during early ontogenesis. Eur J Immunol 44: 1491–1502. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01HL100405/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HG006130/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 DK101665/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL100405/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL032259/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES005605/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL091724/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK098241/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL091724/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01DK098241/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL100001/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01DK093543/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F31 HL120615/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG006130/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK054077/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK093543/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01-HL032259/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1F31HL120615/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
