Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus: epidemiology and disease control measures
- PMID: 25395865
- PMCID: PMC4226520
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S51283
Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus: epidemiology and disease control measures
Abstract
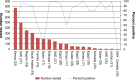
The emergence of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) infection in 2012 resulted in an increased concern of the spread of the infection globally. MERS-CoV infection had previously caused multiple health-care-associated outbreaks and resulted in transmission of the virus within families. Community onset MERS-CoV cases continue to occur. Dromedary camels are currently the most likely animal to be linked to human MERS-CoV cases. Serologic tests showed significant infection in adult camels compared to juvenile camels. The control of MERS-CoV infection relies on prompt identification of cases within health care facilities, with institutions applying appropriate infection control measures. In addition, determining the exact route of transmission from camels to humans would further add to the control measures of MERS-CoV infection.
Keywords: MERS; Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus; Saudi Arabia; control measures; epidemiology; transmission.
Figures
References
-
- Zaki AM1, van Boheemen S, Bestebroer TM, Osterhaus AD, Fouchier RA. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(19):1814–1820. - PubMed
-
- Bermingham A, Chand MA, Brown CS, et al. Severe respiratory illness caused by a novel coronavirus, in a patient transferred to the United Kingdom from the Middle East, September 2012. Euro Surveill. 2012;17(40):20290. - PubMed
-
- Hijawi B, Abdallat M, Sayaydeh A, et al. Novel coronavirus infections in Jordan, April 2012: epidemiological findings from a retrospective investigation. East Mediterr Health J. 2013;19(Suppl 1):S12–S18. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) – update. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2014. [Date accessed July 16, 2014]. Available from: http://www.who.int/csr/don/2014_07_14_mers/en/
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

