Toward patient-centered care: a systematic review of how to ask questions that matter to patients
- PMID: 25396331
- PMCID: PMC4616320
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000120
Toward patient-centered care: a systematic review of how to ask questions that matter to patients
Abstract
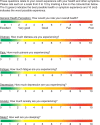
Clinicians rarely systematically document how their patients are feeling. Single item questions have been created to help obtain and monitor patient relevant outcomes, a requirement of patient-centered care.The objective of this review was to identify the psychometric properties for single items related to health aspects that only the patient can report (health perception, stress, pain, fatigue, depression, anxiety, and sleep quality). A secondary objective was to create a bank of valid single items in a format suitable for use in clinical practice.Data sources used were Ovid MEDLINE (1948 to May 2013), EMBASE (1960 to May 2013), and the Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (1960 to May 2013).For the study appraisal, 24 articles were systematically reviewed. A critical appraisal tool was used to determine the quality of articles.Items were included if they were tested as single items, related to the construct, measured symptom severity, and referred to recent experiences.The psychometric properties of each item were extracted. Validity and reliability was observed for the items when compared with clinical interviews or well-validated measures. The items for general health perception and anxiety showed weak to moderate strength correlations (r = 0.28-0.70). The depression and stress items showed good area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.85 and 0.73-0.88, respectively, with high sensitivity and specificity. The fatigue item demonstrated a strong effect size and correlations up to r = 0.80. The 2 pain items and the sleep item showed high reliability (intraclass correlation coefficient [ICC] = 0.85, κ = 0.76, ICC = 0.9, respectively).The search targeted articles about psychometric properties of single items. Articles that did not have this as the primary objective may have been missed. Furthermore, not all the articles included had the complete set of psychometric properties for each item.There is sufficient evidence to warrant the use of single items in clinical practice. They are simple, easily implemented, and efficient and thus provide an alternative to multi-item questionnaires. To facilitate their use, the top performing items were combined into the visual analog health states, which provides a quick profile of how the patient is feeling. This information would be useful for regular long-term monitoring.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. Patient-Centered Outcomes Research. Washington, DC: Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute; 2013.
-
- Greenhalgh J, Meadows K. The effectiveness of the use of patient-based measures of health in routine practice in improving the process and outcomes of patient care: a literature review. J Eval Clin Pract. 1999;5:401–416. - PubMed
-
- McHorney CA, Tarlov AR. Individual-patient monitoring in clinical practice: are available health status surveys adequate? Qual Life Res. 1995;4:293–307. - PubMed
-
- Velikova G, Wright P. Individual patient monitoring. Assessing Quality of Life in Clinical Trials. 2nd ed New York: Oxford University Press; 2005:291–306.
-
- Bennett AV, Jensen RE, Basch E. Electronic patient-reported outcome systems in oncology clinical practice. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:337–347. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical