Comparative analysis of discrete exosome fractions obtained by differential centrifugation
- PMID: 25396408
- PMCID: PMC4224706
- DOI: 10.3402/jev.v3.25011
Comparative analysis of discrete exosome fractions obtained by differential centrifugation
Abstract
Background: Cells release a mixture of extracellular vesicles, amongst these exosomes, that differ in size, density and composition. The standard isolation method for exosomes is centrifugation of fluid samples, typically at 100,000×g or above. Knowledge of the effect of discrete ultracentrifugation speeds on the purification from different cell types, however, is limited.
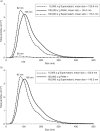
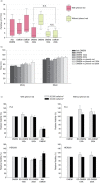
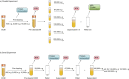
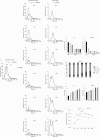
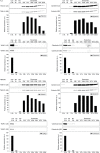
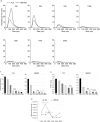
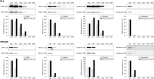
Methods: We examined the effect of applying differential centrifugation g-forces ranging from 33,000×g to 200,000×g on exosome yield and purity, using 2 unrelated human cell lines, embryonic kidney HEK293 cells and bladder carcinoma FL3 cells. The fractions were evaluated by nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), total protein quantification and immunoblotting for CD81, TSG101, syntenin, VDAC1 and calreticulin.
Results: NTA revealed the lowest background particle count in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium media devoid of phenol red and cleared by 200,000×g overnight centrifugation. The centrifugation tube fill level impacted the sedimentation efficacy. Comparative analysis by NTA, protein quantification, and detection of exosomal and contamination markers identified differences in vesicle size, concentration and composition of the obtained fractions. In addition, HEK293 and FL3 vesicles displayed marked differences in sedimentation characteristics. Exosomes were pelleted already at 33,000×g, a g-force which also removed most contaminating microsomes. Optimal vesicle-to-protein yield was obtained at 67,000×g for HEK293 cells but 100,000×g for FL3 cells. Relative expression of exosomal markers (TSG101, CD81, syntenin) suggested presence of exosome subpopulations with variable sedimentation characteristics.
Conclusions: Specific g-force/k factor usage during differential centrifugation greatly influences the purity and yield of exosomes. The vesicle sedimentation profile differed between the 2 cell lines.
Keywords: differential centrifugation; exosomes; extracellular vesicles; k factor; microvesicles; nanoparticle tracking analysis.
Figures
References
-
- Cocucci E, Racchetti G, Meldolesi J. Shedding microvesicles: artefacts no more. Trends Cell Biol. 2009;19:43–51. - PubMed
-
- Thery C, Ostrowski M, Segura E. Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9:581–93. - PubMed
-
- Simpson RJ, Lim JW, Moritz RL, Mathivanan S. Exosomes: proteomic insights and diagnostic potential. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2009;6:267–83. - PubMed
-
- Vlassov AV, Magdaleno S, Setterquist R, Conrad R. Exosomes: current knowledge of their composition, biological functions, and diagnostic and therapeutic potentials. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1820:940–8. - PubMed
-
- Ostenfeld MS. Cellular disposal of miR23b by RAB27-dependent exosome release is linked to acquisition of metastatic properties. Cancer Res. 2014;74:5758–71. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

